Palmitoylation is required for the production of a soluble multimeric Hedgehog protein complex and long-range signaling in vertebrates
- PMID: 15075292
- PMCID: PMC387240
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1185804
Palmitoylation is required for the production of a soluble multimeric Hedgehog protein complex and long-range signaling in vertebrates
Abstract
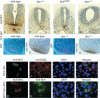
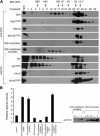
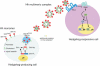
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling plays a major role in multiple aspects of embryonic development. A key issue in Hh signaling is to elucidate the molecular mechanism by which a Hh protein morphogen gradient is formed despite its membrane association. In this study, we used a combination of genetic, cellular, and biochemical approaches to address the role of lipid modifications in long-range vertebrate Hh signaling. Our molecular analysis of knockout mice deficient in Skn, the murine homolog of the Drosophila ski gene, which catalyzes Hh palmitoylation, and gene-targeted mice producing a nonpalmitoylated form of Shh indicates that Hh palmitoylation is essential for its activity as well as the generation of a protein gradient in the developing embryos. Furthermore, our biochemical data show that Hh lipid modifications are required for producing a soluble multimeric protein complex, which constitutes the major active component for Hh signaling. These results suggest that soluble Hh multimeric complex travels in the morphogenetic field to activate Hh signaling in distant Hh-responsive cells.
Figures

References
-
- Amanai K. and Jiang, J. 2001. Distinct roles of Central missing and Dispatched in sending the Hedgehog signal. Development 128: 5119-5127. - PubMed
-
- Ang S.L., Wierda, A., Wong, D., Stevens, K.A., Cascio, S., Rossant, J., and Zaret, K.S. 1993. The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse: Involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development 119: 1301-1315. - PubMed
-
- Bellaiche Y., The, I., and Perrimon, N. 1998. Tout-velu is a Drosophila homologue of the putative tumour suppressor EXT-1 and is needed for Hh diffusion. Nature 394: 85-88. - PubMed
-
- Brand A.H. and Perrimon, N. 1993. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118: 401-415. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J. and Ericson, J. 1999. The specification of neuronal identity by graded Sonic Hedgehog signalling. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 10: 353-362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
