Cell cycle-dependent dynamic localization of a bacterial response regulator with a novel di-guanylate cyclase output domain
- PMID: 15075296
- PMCID: PMC387245
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.289504
Cell cycle-dependent dynamic localization of a bacterial response regulator with a novel di-guanylate cyclase output domain
Abstract
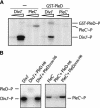
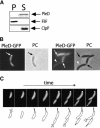
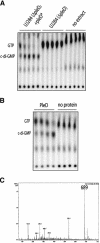
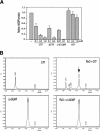
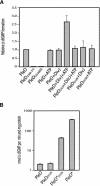
Pole development is coordinated with the Caulobacter crescentus cell cycle by two-component signaling proteins. We show that an unusual response regulator, PleD, is required for polar differentiation and is sequestered to the cell pole only when it is activated by phosphorylation. Dynamic localization of PleD to the cell pole provides a mechanism to temporally and spatially control the signaling output of PleD during development. Targeting of PleD to the cell pole is coupled to the activation of a C-terminal guanylate cyclase domain, which catalyzes the synthesis of cyclic di-guanosine monophosphate. We propose that the local action of this novel-type guanylate cyclase might constitute a general regulatory principle in bacterial growth and development.
Figures
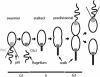

References
-
- Aldridge P. and Jenal, U. 1999. Cell cycle-dependent degradation of a flagellar motor component requires a novel-type response regulator. Mol. Microbiol. 32: 379-391. - PubMed
-
- Aldridge P., Paul, R., Goymer, P., Rainey, P., and Jenal, U. 2003. Role of the GGDEF regulator PleD in polar development of Caulobacter crescentus. Mol. Microbiol. 47: 1695-1708. - PubMed
-
- Anantharaman V. and Aravind, L. 2000. Cache—a signaling domain common to animal Ca2+-channel subunits and a class of prokaryotic chemotaxis receptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25: 535-537. - PubMed
-
- ____. 2001. The CHASE domain: A predicted ligand-binding module in plant cytokinin receptors and other eukaryotic and bacterial receptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26: 579-582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
