The genetic architecture of selection at the human dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene locus
- PMID: 15077199
- PMCID: PMC1181986
- DOI: 10.1086/420854
The genetic architecture of selection at the human dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene locus
Abstract
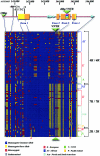
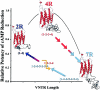
Associations of the seven-repeat (7R) allele of the human dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene with both the personality trait of novelty seeking and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder have been reported. Recently, on the basis of the unusual DNA sequence organization of the DRD4 7R 48-bp tandem repeat (VNTR), we proposed that the 7R allele originated as a rare mutational event that increased to high frequency by positive selection. We now have resequenced the entire DRD4 locus from 103 individuals homozygous for 2R, 4R, or 7R variants of the VNTR, a method developed to directly estimate haplotype diversity. DNA from individuals of African, European, Asian, North and South American, and Pacific Island ancestry were used. 4R/4R homozygotes exhibit little linkage disequilibrium (LD) over the region examined, with more polymorphisms observed in DNA samples from African individuals. In contrast, the evidence for strong LD surrounding the 7R allele is dramatic, with all 7R/7R individuals (including those from Africa) exhibiting the same alleles at most polymorphic sites. By intra-allelic comparison at 18 high-heterozygosity sites spanning the locus, we estimate that the 7R allele arose prior to the upper Paleolithic era (approximately 40000-50000 years ago). Further, the pattern of recombination at these polymorphic sites is the pattern expected for selection acting at the 7R VNTR itself, rather than at an adjacent site. We propose a model for selection at the DRD4 locus consistent with these observed LD patterns and with the known biochemical and physiological differences between receptor variants.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Authors' Web site, http://www.genome.uci.edu(for genotype information)
-
- dbSNP, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/ (for DRD4-140582 [accession number 20399264]; DRD4-140692 [accession number 20399265]; DRD4-140892 [accession number 20399266]; DRD4-140926 [accession number 20399267]; DRD4-140989 [accession number 20399268]; DRD4-141034 [accession number 20399269]; DRD4-141044 [accession number 20399270]; DRD4-141085 [accession number 20399271]; DRD4-141102 [accession number20399272]; DRD4-141182 [accession number 20399273]; DRD4-141183 [accession number 20399274]; DRD4-141195 [accession number 20399275]; DRD4-141204[accession number 20399276]; DRD4-141198 [accessionnumber 20399277]; DRD4-141203 [accession number 20399278]; DRD4-141270 [accession number 20399279]; DRD4-141277 [accession number 20399280]; DRD4-141422 [accession number 20399281]; DRD4-141434[accession number 20399282]; DRD4-141507 [accessionnumber 20399283]; DRD4-141745 [accession number 20399284]; DRD4-141784 [accession number 20399285]; DRD4-141828 [accession number 20399286]; DRD4-142115 [accession number 20399287]; DRD4-142203 accession number 20399288]; DRD4-142347 [accessionnumber 20399289]; DRD4-142426 [accession number20399290]; DRD4-142494 [accession number 20399291]; DRD4-142495 [accession number 20399292]; DRD4-142496 [accession number 20399293]; DRD4-142497[accession number 20399294]; DRD4-142732 [accessionnumber 20399295]; DRD4-142775 [accession number 20399296]; DRD4-142940 [accession number 203992697]; DRD4-142976 [accession number 20399298]; DRD4-143118 [accession number 20399299]; DRD4-143318[accession number 20399300]; DRD4-143348 [accessionnumber 20399301]; DRD4-143578 [accession number 20399302]; DRD4-143766 [accession number 20399303]; DRD4-143862 [accession number 20399304]; DRD4-143870 [accession number 20399305]; DRD4-143867[accession number 20399306]; DRD4-143058 [accessionnumber 20399307]; DRD4-143060 [accession number 20399308]; DRD4-144054 [accession number 20399309]; DRD4-144746 [accession number 20399310]; DRD4-144842 [accession number 20399311]; DRD4-144843[accession number 20399312]; DRD4-144862 [accessionnumber 20399313]; DRD4-145239 [accession number 20399314]; DRD4-145295 [accession number 20399315];DRD4-145298 [accession number 20399316]; DRD4-145334 [accession number 20399317]; DRD4-145353[accession number 20399318]; DRD4-145365 [accession number 20399319]; DRD4-145417 [accession number 20399320]; DRD4-145430 [accession number 20399321]; DRD4-145568 [accession number 20399322]; DRD4-145651 [accession number 20399323]; DRD4-145684[accession number 20399324]; DRD4-146033 [accessionnumber 20399325]; DRD4-146041 [accession number 20399326]; DRD4-146056 [accession number 20399327]; DRD4-146140 [accession number 20399328]; DRD4-146158 [accession number 20399329]; DRD4-146289 [accession number 20399330]; and DRD4-146293 [accession number 20399331]; dbSNP handle: rmoyzis)
References
-
- Asghari V, Sanyal S, Buchwaldt S, Paterson A, Jovanovic V, Van Tol HH (1995) Modulation of intercellular cyclic AMP levels by different human dopamine D4 receptor variants. J Neurochem 65:1157–1165 - PubMed
-
- Betzig L (1993) Sex, succession and stratification in the first six civilizations. In: Ellis L (ed) Social stratification and socioeconomic inequality. Praeger, Westport, CT, pp 37–74
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

