Haplotype block partitioning and tag SNP selection using genotype data and their applications to association studies
- PMID: 15078859
- PMCID: PMC479119
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1837404
Haplotype block partitioning and tag SNP selection using genotype data and their applications to association studies
Abstract
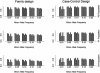
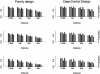
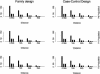
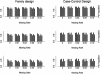
Recent studies have revealed that linkage disequilibrium (LD) patterns vary across the human genome with some regions of high LD interspersed by regions of low LD. A small fraction of SNPs (tag SNPs) is sufficient to capture most of the haplotype structure of the human genome. In this paper, we develop a method to partition haplotypes into blocks and to identify tag SNPs based on genotype data by combining a dynamic programming algorithm for haplotype block partitioning and tag SNP selection based on haplotype data with a variation of the expectation maximization (EM) algorithm for haplotype inference. We assess the effects of using either haplotype or genotype data in haplotype block identification and tag SNP selection as a function of several factors, including sample size, density or number of SNPs studied, allele frequencies, fraction of missing data, and genotyping error rate, using extensive simulations. We find that a modest number of haplotype or genotype samples will result in consistent block partitions and tag SNP selection. The power of association studies based on tag SNPs using genotype data is similar to that using haplotype data.
Figures



References
-
- Abecasis, G.R. and Cookson, W.O. 2000. GOLD—Graphical overview of linkage disequilibrium. Bioinformatics 16: 182-183. - PubMed
-
- Cardon, L.R., Ke, X., Lawrence, R., Carter, N., Rogers, J., Stavrides, G., Willey, D., Mullikin, J., Hunt, S., Bentley, D.R., et al. 2003. Towards a fine-scale linkage disequilibrium map of human chromosome 20. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73 (Suppl): 271. - PubMed
-
- Clark, A.G. 1990. Inference of haplotypes from PCR-amplified samples of diploid populations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 7: 111-122. - PubMed
-
- Daly, M.J., Rioux, J.D., Schaffner, S.F., Hudson, T.J., and Lander, E.S. 2001. High-resolution haplotype structure in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 29: 229-232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
