Network motifs in integrated cellular networks of transcription-regulation and protein-protein interaction
- PMID: 15079056
- PMCID: PMC395901
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0306752101
Network motifs in integrated cellular networks of transcription-regulation and protein-protein interaction
Abstract
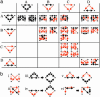
Genes and proteins generate molecular circuitry that enables the cell to process information and respond to stimuli. A major challenge is to identify characteristic patterns in this network of interactions that may shed light on basic cellular mechanisms. Previous studies have analyzed aspects of this network, concentrating on either transcription-regulation or protein-protein interactions. Here we search for composite network motifs: characteristic network patterns consisting of both transcription-regulation and protein-protein interactions that recur significantly more often than in random networks. To this end we developed algorithms for detecting motifs in networks with two or more types of interactions and applied them to an integrated data set of protein-protein interactions and transcription regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We found a two-protein mixed-feedback loop motif, five types of three-protein motifs exhibiting coregulation and complex formation, and many motifs involving four proteins. Virtually all four-protein motifs consisted of combinations of smaller motifs. This study presents a basic framework for detecting the building blocks of networks with multiple types of interactions.
Figures

References
-
- Thieffry, D., Huerta, A. M., Perez-Rueda, E. & Collado-Vides, J. (1998) BioEssays 20, 433–440. - PubMed
-
- Fell, D. A. & Wagner, A. (2000) Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 1121–1122. - PubMed
-
- Guelzim, N., Bottani, S., Bourgine, P. & Kepes, F. (2002) Nat. Genet. 31, 60–63. - PubMed
-
- Uetz, P., Giot, L., Cagney, G., Mansfield, T. A., Judson, R. S., Knight, J. R., Lockshon, D., Narayan, V., Srinivasan, M., Pochart, P., et al. (2000) Nature 403, 623–627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

