Epidermal growth factor receptor stimulation activates the RNA binding protein CUG-BP1 and increases expression of C/EBPbeta-LIP in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 15082764
- PMCID: PMC387752
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.9.3682-3691.2004
Epidermal growth factor receptor stimulation activates the RNA binding protein CUG-BP1 and increases expression of C/EBPbeta-LIP in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
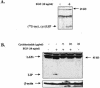
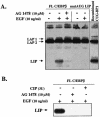
The transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBP beta) is a key regulator of growth and differentiation in many tissues. C/EBP beta is expressed as several distinct protein isoforms (LAP1, LAP2, and LIP) whose expression is regulated by alternative translational initiation at downstream AUG start sites. The dominant-negative LIP isoform is predominantly expressed during proliferative cellular responses and is associated with aggressive tumors. In this study, we investigated a mechanism by which the LIP isoform is translationally regulated in mammary epithelial cells. We have demonstrated that LIP expression is increased in response to activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway and that the increased expression of LIP is regulated in part by an RNA binding protein referred to as CUG repeat binding protein (CUG-BP1). Our data demonstrate that EGFR signaling results in the phosphorylation of CUG-BP1 and this leads to an increase in the binding of CUG-BP1 to C/EBP beta mRNA and elevated expression of the LIP isoform. Phosphorylation is necessary for the binding activity of CUG-BP1 and the consequent increase in LIP expression, as determined by binding assays and a cell free, transcription-coupled translation system. CUG-BP1 is thus a previously unidentified downstream target of EGFR signaling and represents a new translational regulator of LIP expression in human mammary epithelial cells.
Figures







References
-
- Alaoui-Jamali, M. A., D. J. Song, N. Benlimame, L. Yen, X. Deng, M. Hernandez-Perez, and T. Wang. 2003. Regulation of multiple tumor microenvironment markers by overexpression of single or paired combinations of ErbB receptors. Cancer Res. 63:3764-3774. - PubMed
-
- Badley, J. E., G. A. Bishop, T. St John, and J. A. Frelinger. 1988. A simple, rapid method for the purification of poly A+ RNA. BioTechniques 6:114-116. - PubMed
-
- Baer, M., and P. F. Johnson. 2000. Generation of truncated C/EBPβ isoforms by in vitro proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 275:26582-26590. - PubMed
-
- Bundy, L. M., and L. Sealy. 2003. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBPβ)-2 transforms normal mammary epithelial cells and induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in culture. Oncogene 22:869-883. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
