Acquired expression of periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression
- PMID: 15082792
- PMCID: PMC387763
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.9.3992-4003.2004
Acquired expression of periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression
Abstract
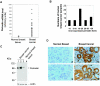
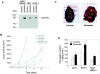
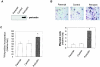
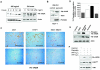
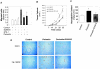
The late stages of human breast cancer development are poorly understood complex processes associated with the expression of genes by cancers that promote specific tumorigenic activities, such as angiogenesis. Here, we describe the identification of periostin as a mesenchyme-specific gene whose acquired expression by human breast cancers leads to a significant enhancement in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Undetectable in normal human breast tissues, periostin was found to be overexpressed by the vast majority of human primary breast cancers examined. Tumor cell lines engineered to overexpress periostin showed a phenotype of accelerated growth and angiogenesis as xenografts in immunocompromised animals. The underlying mechanism of periostin-mediated induction of angiogenesis was found to derive in part from the up-regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flk-1/KDR by endothelial cells through an integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-focal adhesion kinase-mediated signaling pathway. These findings demonstrate the presence of a novel mechanism by which tumor angiogenesis is acquired with the expression of a mesenchyme-specific gene as a crucial step in late stages of tumorigenesis.
Figures


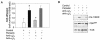
References
-
- Biroccio, A., A. Candiloro, M. Mottolese, O. Sapora, A. Albini, G. Zupi, and D. Del Bufalo. 2000. Bcl-2 overexpression and hypoxia synergistically act to modulate vascular endothelial growth factor expression and in vivo angiogenesis in a breast carcinoma line. FASEB J. 14:652-660. - PubMed
-
- Dougher, M., and B. I. Terman. 1999. Autophosphorylation of KDR in the kinase domain is required for maximal VEGF-stimulated kinase activity and receptor internalization. Oncogene 18:1619-1627. - PubMed
-
- Folkman, J. 1996. Tumor angiogenesis and tissue factor. Nat. Med. 2:167-168. - PubMed
-
- Folkman, J., K. Watson, D. Ingber, and D. Hanahan. 1989. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature 339:58-61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
