Reproducibility of a novel model of murine asthma-like pulmonary inflammation
- PMID: 15086384
- PMCID: PMC1809026
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02461.x
Reproducibility of a novel model of murine asthma-like pulmonary inflammation
Abstract
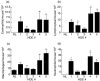
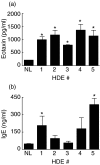
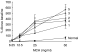
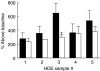
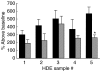
Sensitization to cockroach allergens (CRA) has been implicated as a major cause of asthma, especially among inner-city populations. Endotoxin from Gram-negative bacteria has also been investigated for its role in attenuating or exacerbating the asthmatic response. We have created a novel model utilizing house dust extract (HDE) containing high levels of both CRA and endotoxin to induce pulmonary inflammation (PI) and airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR). A potential drawback of this model is that the HDE is in limited supply and preparation of new HDE will not contain the exact components of the HDE used to define our model system. The present study involved testing HDEs collected from various homes for their ability to cause PI and AHR. Dust collected from five homes was extracted in phosphate buffered saline overnight. The levels of CRA and endotoxin in the supernatants varied from 7.1 to 49.5 mg/ml of CRA and 1.7-6 micro g/ml of endotoxin in the HDEs. Following immunization and two pulmonary exposures to HDE all five HDEs induced AHR, PI and plasma IgE levels substantially higher than normal mice. This study shows that HDE containing high levels of cockroach allergens and endotoxin collected from different sources can induce an asthma-like response in our murine model.
Figures
References
-
- Bernton HS, McMahon TF, Brown H. Cockroach asthma. Br J Dis Chest. 1972;66:61–6. - PubMed
-
- Rosenstreich DL, Eggleston P, Kattan M, et al. The role of cockroach allergy and exposure to cockroach allergen in causing morbidity among inner-city children with asthma [see comments] N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1356–63. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Zhou D, Kang BC. A comparative study on cockroach and ovalbumin sensitizations and challenge responses in Hartley guinea-pigs. Respir Physiol. 2001;125:239–47. - PubMed
-
- Ernst P, Cormier Y. Relative scarcity of asthma and atopy among rural adolescents raised on a farm. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:1563–6. - PubMed
-
- Kramer U, Heinrich J, Wjst M, Wichmann HE. Age of entry to day nursery and allergy in later childhood. Lancet. 1999;353:450–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

