Differential expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR-4 on monocytes in human sepsis
- PMID: 15086396
- PMCID: PMC1809013
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02433.x
Differential expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR-4 on monocytes in human sepsis
Abstract
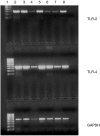
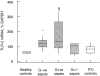
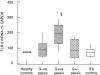
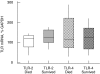
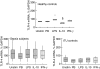
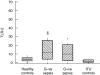
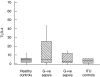
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a recently described family of immune receptors involved in the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). The central role of TLR-2 and TLR-4 in microbial responses suggests they may be implicated in the pathogenesis of human sepsis. We hypothesized that the incidence and outcome of sepsis would be influenced by the expression of TLR-2 and TLR-4 on monocytes. We have examined the expression of TLR-2 and TLR-4 mRNA and protein and their response to pro- and anti-inflammatory agents on monocytes from subjects in the intensive therapy unit (ITU) with and without Gram-negative, Gram-positive or polymicrobial sepsis. We compared these data to ITU and healthy control subjects. TLR-2 mRNA was significantly up-regulated on monocytes from subjects with both Gram-positive and Gram-negative sepsis. Similarly, we detected increased levels of TLR-2 protein on the surface of monocytes from sepsis subjects relative to ITU controls. TLR-4 mRNA was increased in Gram-positive subjects; however, there was no corresponding increase in TLR-4 protein. Although TLR-4 mRNA expression in healthy control monocytes could be modulated in vitro by culture with lipopolysaccharide or interleukin-10, this was not observed in monocytes obtained from sepsis and ITU control subjects, suggesting that septic and ITU control milieus may alter the immunoregulation of TLR-4 mRNA expression on monocytes. TLR-2 mRNA was not modulated in culture by any stimulus in any group. We suggest that expression and regulatory response of monocyte TLR-2, and to a lesser extent TLR-4 may be abnormal in human sepsis.
Figures


References
-
- Means TK, Golenbock DT, Fenton MJ. Structure and function of Toll-like receptor proteins. Life Sci. 2000;68:241–58. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill L. The Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain: a molecular switch for inflammation and host defence. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28:557–63. - PubMed
-
- Chow JC, Young DW, Golenbock DT, Christ WJ, Gusovsky F. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:10689–92. - PubMed
-
- Lien E, Sellati TJ, Yoshimura A, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 functions as a pattern recognition receptor for diverse bacterial products. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:33419–25. - PubMed
-
- Underhill DM, Ozinsky A, Hajjar AM, et al. The Toll-like receptor 2 is recruited to macrophage phagosomes and discriminates between pathogens. Nature. 1999;401:811–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

