Primary immune response to keyhole limpet haemocyanin following trauma in relation to low plasma glutamine
- PMID: 15086402
- PMCID: PMC1809027
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02447.x
Primary immune response to keyhole limpet haemocyanin following trauma in relation to low plasma glutamine
Abstract
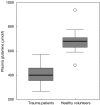
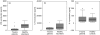
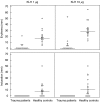
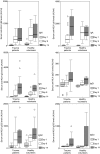
Severe trauma can lead to a compromised immune response, thereby increasing susceptibility to infections. Here we will study to what extent these early changes in the immune status upon trauma affect a primary immune response to keyhole limpet haemocyanin (KLH). Because glutamine is the preferred respiratory substrate for immune competent cells and known to be depleted after trauma, we studied the immune status and the primary sensitization in relation to the glutamine plasma concentration in a group of severe trauma patients [injury severity score (ISS) >17]. Trauma patients (n = 31) were sensitized with KLH within 12 h after trauma; plasma glutamine concentrations and immune parameters were determined, after which KLH-specific immune responsiveness was evaluated on days 9 and 14. Low plasma glutamine concentrations were found after trauma. Significantly elevated numbers of granulocytes and CD14-positive leucocytes were found, whereas the HLA-DR expression on CD14-positive cells was significantly lower in trauma patients than in healthy controls. Trauma did not change the in vitro proliferative capacity of lymphocytes when cultured with glutamine; however, when lymphocytes were cultured without glutamine, trauma resulted in lower proliferation than healthy controls. Phytohaemagglutinin-(PHA)-induced interferon (IFN)-gamma and interleukin (IL)-10 production was significantly lower after trauma, whereas IL-4 production was not affected. KLH sensitization following trauma resulted in poor skin test reactivity and low in vitro KLH-induced lymphocyte proliferation compared to controls. In contrast, the development of anti-KLH IgM, IgG, IgA, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 production on days 9 and 14 following trauma was not different from that in healthy controls. Major trauma was associated with a reduced cell-mediated immune response, correlating with low plasma glutamine concentrations, while no effects of trauma were found on the development of a primary humoral immune response.
Figures

References
-
- Bone RC. Immunologic dissonance: a continuing evolution in our understanding of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) Ann Intern Med. 1996;125:680–7. - PubMed
-
- Ardawi MS. Glutamine and glucose metabolism in human peripheral lymphocytes. Metabolism. 1988;37:99–103. - PubMed
-
- Harris JR, Markl J. Keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH): a biomedical review. Micron. 1999;30:597–623. - PubMed
-
- Meakins JL, McLean AP, Kelly R, Bubenik O, Pietsch JB, MacLean LD. Delayed hypersensitivity and neutrophil chemotaxis: effect of trauma. J Trauma. 1978;18:240–7. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe JH, Wu AV, O'Connor NE, Saporoschetz I, Mannick JA. Anergy, immunosuppressive serum, and impaired lymphocyte blastogenesis in burn patients. Arch Surg. 1982;117:1266–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

