Real-time PCR genotyping using displacing probes
- PMID: 15087493
- PMCID: PMC407835
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh055
Real-time PCR genotyping using displacing probes
Abstract
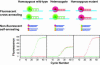
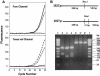
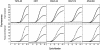
Simple and reliable genotyping technology is a key to success for high-throughput genetic screening in the post-genome era. Here we have developed a new real-time PCR genotyping approach that uses displacement hybridization-based probes: displacing probes. The specificity of displacing probes could be simply assessed through denaturation analysis before genotyping was implemented, and the probes designed with maximal specificity also showed the greatest detection sensitivity. The ease in design, the simple single-dye labeling chemistry and the capability to adopt degenerated negative strands for point mutation genotyping make the displacing probes both cost effective and easy to use. The feasibility of this method was first tested by detecting the C282Y mutation in the human hemochromatosis gene. The robustness of this approach was then validated by simultaneous genotyping of five different types of mutation in the human beta-globin gene. Sixty-two human genomic DNA samples with nine known genotypes were accurately detected, 32 random clinical samples were successfully screened and 114 double-blind DNA samples were all correctly genotyped. The combined merits of reliability, flexibility and simplicity should make this method suitable for routine clinical testing and large-scale genetic screening.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Real-time PCR genotyping of aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 using displacing probes.Clin Biochem. 2007 Nov;40(16-17):1325-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Aug 10. Clin Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17854793
-
Multicolor real-time polymerase chain reaction genotyping of six human platelet antigens using displacing probes.Transfusion. 2007 Sep;47(9):1637-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2007.01335.x. Transfusion. 2007. PMID: 17725728
-
Rapid genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms using novel minor groove binding DNA oligonucleotides (MGB probes).Hum Mutat. 2002 May;19(5):554-9. doi: 10.1002/humu.10076. Hum Mutat. 2002. PMID: 11968088
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using locked nucleic acid (LNA).Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003 Jan;3(1):27-38. doi: 10.1586/14737159.3.1.27. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003. PMID: 12528362 Review.
-
High and intermediate resolution DNA typing systems for class I HLA-A, B, C genes by hybridization with sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes (SSOP).Rev Immunogenet. 1999;1(2):177-208. Rev Immunogenet. 1999. PMID: 11253946 Review.
Cited by
-
Thermodynamically modulated partially double-stranded linear DNA probe design for homogeneous real-time PCR.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(16):e101. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm551. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17693434 Free PMC article.
-
Use of duplex mutation primers for real-time PCR quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum.Hepat Mon. 2011 Jul;11(7):519-24. Hepat Mon. 2011. PMID: 22087189 Free PMC article.
-
ZnO Nanolower-Based NanoPCR as an Efficient Diagnostic Tool for Quick Diagnosis of Canine Vector-Borne Pathogens.Pathogens. 2020 Feb 14;9(2):122. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9020122. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32075178 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the Bacillus atrophaeus subsp. globigii Spo0F H101R mutation on strain fitness.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Dec;78(24):8601-10. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01922-12. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23042165 Free PMC article.
-
Seven novel probe systems for real-time PCR provide absolute single-base discrimination, higher signaling, and generic components.J Mol Diagn. 2014 Nov;16(6):627-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2014.06.008. J Mol Diagn. 2014. PMID: 25307756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiss K.M. (1998) In search of human variation. Genome Res., 8, 691–697. - PubMed
-
- Mir K.U. and Southern,E.M. (2000) Sequence variation in genes and genomic DNA: methods for large-scale analysis. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet., 1, 329–360. - PubMed
-
- Kwok P.Y. (2000) High-throughput genotyping assay approaches. Pharmacogenomics, 1, 95–100. - PubMed
-
- Foy C.A. and Parkes,H.C. (2001) Emerging homogeneous DNA-based technologies in the clinical laboratory. Clin. Chem., 47, 990–1000. - PubMed
-
- Germer S. and Higuchi,R. (2003) Homogeneous allele-specific PCR in SNP genotyping. Methods Mol. Biol., 212, 197–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

