Small Maf proteins serve as transcriptional cofactors for keratinocyte differentiation in the Keap1-Nrf2 regulatory pathway
- PMID: 15087497
- PMCID: PMC404053
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0305902101
Small Maf proteins serve as transcriptional cofactors for keratinocyte differentiation in the Keap1-Nrf2 regulatory pathway
Abstract
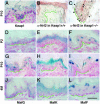
The small Maf proteins, MafF, MafG, and MafK, possess a leucine zipper (Zip) domain that is required for homodimer or heterodimer complex formation with other bZip transcription factors. In this study we sought to determine the identity of the specific constituent that collaboratively interacts with Nrf2 to bind to the Maf recognition element in vivo. Studies in vitro suggested that Nrf2 forms heterodimers with small Maf proteins and then bind to Maf recognition elements, but the bona fide partner molecules supporting Nrf2 activity in vivo have not been definitively identified. Nrf2 activity is usually suppressed by a cytoplasmic repressor, Keap1, so disruption of the keap1 gene causes constitutive activation of Nrf2. Nrf2 hyperactivity results in hyperproliferation of keratinocytes in the esophagus and forestomach leading to perinatal lethality. However, simultaneous disruption of nrf2 rescued keap1-null mice from the lethality. We exploited this system to investigate whether small Mafs are required for Nrf2 function. We generated keap1 and small maf compound mutant mice and examined whether keratinocyte abnormalities persisted in these animals. The data show that loss of mafG and mafF in the keap1-null mice reversed the lethal keratinocyte dysfunction and rescued the keap1-null mutant mice from perinatal lethality. This rescue phenotype of mafG::mafF::keap1 triple compound mutant mice phenocopies that of the nrf2::keap1 compound mutant mice, indicating that the small Maf proteins MafG and MafF must functionally cooperate with Nrf2 in vivo.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genetic evidence that small maf proteins are essential for the activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;25(18):8044-51. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.18.8044-8051.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16135796 Free PMC article.
-
Keap1-null mutation leads to postnatal lethality due to constitutive Nrf2 activation.Nat Genet. 2003 Nov;35(3):238-45. doi: 10.1038/ng1248. Epub 2003 Sep 28. Nat Genet. 2003. PMID: 14517554
-
Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism.Trends Mol Med. 2004 Nov;10(11):549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.09.003. Trends Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15519281 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004 May 15;36(10):1208-13. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.02.075. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15110385 Review.
-
Arsenic induces NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase I by disrupting the Nrf2 x Keap1 x Cul3 complex and recruiting Nrf2 x Maf to the antioxidant response element enhancer.J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 18;281(33):23620-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604120200. Epub 2006 Jun 19. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16785233
Cited by
-
The Functional Significance of McMafF_G_K in Molluscs: Implications for Nrf2-Mediated Oxidative Stress Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 27;24(23):16800. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316800. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069123 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives on the therapeutic potential of quercetin in non-communicable diseases: Targeting Nrf2 to counteract oxidative stress and inflammation.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Jun;14(6):100930. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.12.020. Epub 2024 Jan 3. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39005843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carcinogenesis and transcriptional regulation through Maf recognition elements.Cancer Sci. 2007 Feb;98(2):135-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00358.x. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Cancer Sci. 2007. PMID: 17129360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Phytochemicals Targeting Nrf2 to Enhance the Radiosensitivity of Cancer.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 23;2022:7848811. doi: 10.1155/2022/7848811. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35368867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2 in cancers: A double-edged sword.Cancer Med. 2019 May;8(5):2252-2267. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2101. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30929309 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

