Substrate-specifying determinants of the nucleotide pyrophosphatases/phosphodiesterases NPP1 and NPP2
- PMID: 15096095
- PMCID: PMC1133763
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040465
Substrate-specifying determinants of the nucleotide pyrophosphatases/phosphodiesterases NPP1 and NPP2
Erratum in
-
Correction: Substrate-specifying determinants of the nucleotide pyrophosphatases/phosphodiesterases NPP1 and NPP2.Biochem J. 2017 Dec 14;474(24):4273-4274. doi: 10.1042/BCJ-2004-0465_COR. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 29242384 No abstract available.
Abstract
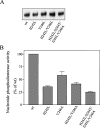
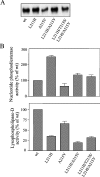
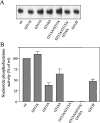
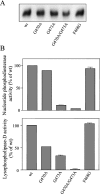
The nucleotide pyrophosphatases/phosphodiesterases NPP1 and NPP2/autotaxin are structurally related eukaryotic ecto-enzymes, but display a very different substrate specificity. NPP1 releases nucleoside 5'-monophosphates from various nucleotides, whereas NPP2 mainly functions as a lysophospholipase D. We have used a domain-swapping approach to map substrate-specifying determinants of NPP1 and NPP2. The catalytic domain of NPP1 fused to the N- and C-terminal domains of NPP2 was hyperactive as a nucleotide phosphodiesterase, but did not show any lysophospholipase D activity. In contrast, chimaeras of the catalytic domain of NPP2 and the N- and/or C-terminal domains of NPP1 were completely inactive. These data indicate that the catalytic domain as well as both extremities of NPP2 contain lysophospholipid-specifying sequences. Within the catalytic domain of NPP1 and NPP2, we have mapped residues close to the catalytic site that determine the activities towards nucleotides and lysophospholipids. We also show that the conserved Gly/Phe-Xaa-Gly-Xaa-Xaa-Gly (G/FXGXXG) motif near the catalytic site is required for metal binding, but is not involved in substrate-specification. Our data suggest that the distinct activities of NPP1 and NPP2 stem from multiple differences throughout the polypeptide chain.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The hydrolysis of lysophospholipids and nucleotides by autotaxin (NPP2) involves a single catalytic site.FEBS Lett. 2003 Mar 13;538(1-3):60-4. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00133-9. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12633853
-
Structure of NPP1, an ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase involved in tissue calcification.Structure. 2012 Nov 7;20(11):1948-59. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.09.001. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Structure. 2012. PMID: 23041369
-
Proteolytic maturation and activation of autotaxin (NPP2), a secreted metastasis-enhancing lysophospholipase D.J Cell Sci. 2005 Jul 15;118(Pt 14):3081-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02438. Epub 2005 Jun 28. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15985467
-
Nucleotide pyrophosphatases/phosphodiesterases on the move.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2000;35(6):393-432. doi: 10.1080/10409230091169249. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11202013 Review.
-
Physiological and pathophysiological functions of the ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 May 20;1638(1):1-19. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(03)00058-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12757929 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (NPP1) and its inhibitors.Medchemcomm. 2017 Feb 9;8(5):823-840. doi: 10.1039/c7md00015d. eCollection 2017 May 1. Medchemcomm. 2017. PMID: 30108800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophospholipid interactions with protein targets.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Sep;1781(9):540-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.04.011. Epub 2008 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18501204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human antibodies targeting ENPP1 as candidate therapeutics for cancers.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 25;14:1070492. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1070492. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36761762 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of autotaxin/lysophospholipase d inhibitors.Curr Drug Targets. 2008 Aug;9(8):698-708. doi: 10.2174/138945008785132439. Curr Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18691016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substrate-Dependence of Competitive Nucleotide Pyrophosphatase/Phosphodiesterase1 (NPP1) Inhibitors.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Feb 15;8:54. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00054. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28261095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bollen M., Gijsbers R., Ceulemans H., Stalmans W., Stefan C. Nucleotide pyrophosphatases/phosphodiesterases on the move. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000;35:393–432. - PubMed
-
- Gijsbers R., Ceulemans H., Stalmans W., Bollen M. Structural and catalytic similarities between nucleotide pyrophosphatases/phosphodiesterases and alkaline phosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:1361–1368. - PubMed
-
- Duan R.-D., Bergman T., Xu N., Wu J., Cheng Y., Duan J., Nelander S., Palmberg C., Nilsson A. Identification of human intestinal alkaline sphingomyelinase as a novel ecto-enzyme related to the nucleotide phosphodiesterase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:38528–38536. - PubMed
-
- Goding J. W., Grobben B., Slegers H. Physiological and pathophysiological functions of the ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2003;1638:1–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

