An efficient system for high-level expression and easy purification of authentic recombinant proteins
- PMID: 15096636
- PMCID: PMC2286746
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.04618904
An efficient system for high-level expression and easy purification of authentic recombinant proteins
Abstract
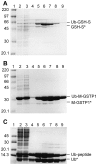
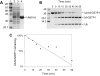
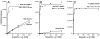
Expression of recombinant proteins as fusions to the eukaryotic protein ubiquitin has been found to significantly increase the yield of unstable or poorly expressed proteins. The benefit of this technique is further enhanced by the availability of naturally occurring deubiquitylating enzymes, which remove ubiquitin from the fusion product. However, the versatility of the system has been constrained due to the lack of a robust, easily purified deubiquitylating enzyme. Here we report the development of an efficient expression system, utilizing the ubiquitin fusion technique, which allows convenient high yield and easy purification of authentic protein. An Escherichia coli vector (pHUE) was constructed for the expression of proteins as histidine-tagged ubiquitin fusions, and a histidine-tagged deubiquitylating enzyme to cleave these fusions was expressed and purified. The expression system was tested using several proteins varying in size and complexity. These results indicate that this procedure will be suitable for the expression and rapid purification of a broad range of proteins and peptides, and should be amenable to high-throughput applications.
Figures


References
-
- Bachmair, A., Finley, D., and Varshavsky, A. 1986. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science 234 179–186. - PubMed
-
- Baker, R.T. 1996. Protein expression using ubiquitin fusion and cleavage. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 7 541–546. - PubMed
-
- Baker, R.T. and Varshavsky, A. 1995. Yeast N-terminal amidase. A new enzyme and component of the N-end rule pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 270 12065–12074. - PubMed
-
- Baker, R.T., Smith, S.A., Marano, R., McKee, J., and Board, P.G. 1994. Protein expression using cotranslational fusion and cleavage of ubiquitin. Mutagenesis of the glutathione-binding site of human Pi class glutathione S-transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 269 25381–25386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

