Methylamine, but not ammonia, is hypophagic in mouse by interaction with brain Kv1.6 channel subtype
- PMID: 15100162
- PMCID: PMC1574941
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705740
Methylamine, but not ammonia, is hypophagic in mouse by interaction with brain Kv1.6 channel subtype
Abstract
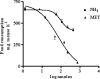
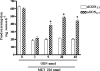
Ammonia and methylamine (MET) are endogenous compounds increased during liver and renal failure, Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia and diabetes, where they alter some neurobehavioural functions probably acting as potassium channel blockers. We have already described that potassium channel blockers including tetraethylammonium (TEA), ammonia and MET are hypophagic in mice. Antisense oligonucleotides (aODNs) against Shaker-like Kv1.1 gene abolished the effect of TEA but not of ammonia and MET. The central effects elicited in fasted mice by ammonia and MET were further studied. For MET, an ED(50) value 71.4+/-1.8 nmol mouse(-1) was calculated. The slope of the dose-response curves for these two compounds and the partial hypophagic effect elicited by ammonia indicated a different action mechanism for these amines. The aODNs pretreatments capable of temporarily reducing the expression of all seven known subtypes of Shaker-like gene or to inactivate specifically the Kv1.6 subtype abolished the hypophagic effect of MET but not that of ammonia. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, Western blot and immunohistochemical results indicate that a full expression in the brain of Kv1.6 is required only for the activity of MET, and confirms the different action mechanism of ammonia and MET.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Methylamine-dependent release of nitric oxide and dopamine in the CNS modulates food intake in fasting rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Apr;150(8):1003-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707170. Epub 2007 Mar 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17339841 Free PMC article.
-
Methylamine and benzylamine induced hypophagia in mice: modulation by semicarbazide-sensitive benzylamine oxidase inhibitors and aODN towards Kv1.1 channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct;134(4):880-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704316. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11606329 Free PMC article.
-
An antisense oligonucleotide on the mouse Shaker-like potassium channel Kv1.1 gene prevents antinociception induced by morphine and baclofen.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 May;281(2):941-9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 9152404
-
4-methyl benzylamine stimulates food consumption and counteracts the hypophagic effects of amphetamine acting on brain Shaker-like Kv1.1 channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147(2):218-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706465. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16284626 Free PMC article.
-
Methylamine: a new endogenous modulator of neuron firing?Med Sci Monit. 2005 Aug;11(8):RA257-61. Epub 2005 Jul 25. Med Sci Monit. 2005. PMID: 16049393 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylamine-dependent release of nitric oxide and dopamine in the CNS modulates food intake in fasting rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Apr;150(8):1003-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707170. Epub 2007 Mar 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17339841 Free PMC article.
-
Methylamine induced hypophagia is mediated via dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in neonatal meat chicks.Vet Res Commun. 2016 Mar;40(1):21-7. doi: 10.1007/s11259-015-9649-y. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Vet Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26685977
-
Utilizing NMR fecal metabolomics as a novel technique for detecting the physiological effects of food shortages in waterfowl.Front Physiol. 2024 Jan 10;14:1229152. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1229152. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38269059 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of impaired olfactory function in ESRD to malnutrition and retained uremic molecules.Am J Kidney Dis. 2008 Jul;52(1):102-10. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.02.301. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008. PMID: 18423810 Free PMC article.
-
Retained organic solutes, patient characteristics and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hemodialysis: results from the retained organic solutes and clinical outcomes (ROSCO) investigators.BMC Nephrol. 2013 Jun 27;14:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-134. BMC Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23806101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AGUILAR M.A. Chronic moderate hyperammoniemia impairs active and passive avoidance behavior and conditional discrimination learning in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2000;161:704–713. - PubMed
-
- BABA S., WATANABE Y., GEJYO F., ARAKWA M. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of serum aliphatic amines in chronic renal failure. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1984;136:49–56. - PubMed
-
- BANCHELLI G., GHELARDINI C., RAIMONDI L., GALEOTTI N., PIRISINO R. Selective inhibition of amine oxidases differently potentiate the hypophagic effect of benzylamine in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001;413:91–99. - PubMed
-
- BASILE A.S. Direct and indirect enhancement of GABAergic neurotransmission by ammonia: implications for the pathogenesis of hyperammonemic syndromes. Neurochem. Int. 2002;41:115–122. - PubMed
-
- BUFFONI F. Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidases: some biochemical properties and general considerations. Prog. Brain Res. 1995;106:323–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

