Distinctive roles for 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetases and double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase R in the in vivo antiviral effect of an adenoviral vector expressing murine IFN-beta
- PMID: 15100308
- PMCID: PMC4060620
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5638
Distinctive roles for 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetases and double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase R in the in vivo antiviral effect of an adenoviral vector expressing murine IFN-beta
Abstract
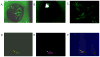
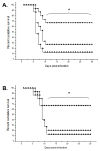
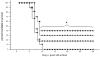
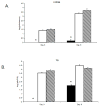
To evaluate the anti-HSV-1 mechanisms of murine IFN-beta in ocular infection, mice were transduced with an adenoviral vector expressing murine IFN-beta (Ad:IFN-beta). Ocular transduction with Ad:IFN-beta resulted in enhanced survival following infection with HSV-1. The protective effect was associated with a reduction in 1) viral titer, 2) viral gene expression, 3) IFN-gamma levels, and 4) the percentage of CD8(+) T lymphocyte and NK cell infiltration in infected tissue. Expression of IFN-beta resulted in an elevation of the IFN-induced antiviral gene 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS1a) but not dsRNA-dependent protein kinase R (PKR) in the cornea and trigeminal ganglion (TG). Mice deficient in the downstream effector molecule of the OAS pathway, RNase L, were no more sensitive to ocular HSV-1 compared with wild-type controls in the TG based on measurements of viral titer. However, the efficacy of Ad:IFN-beta was transiently lost in the eyes of RNase L mice. By comparison, PKR-deficient mice were more susceptible to ocular HSV-1 infection, and the antiviral efficacy following transduction with Ad:IFN-beta was significantly diminished in the eye and TG. These results suggest that PKR is central in controlling ocular HSV-1 infection in the absence of exogenous IFN, whereas the OAS pathway appears to respond to exogenous IFN, contributing to the establishment of an antiviral environment in a tissue-restricted manner.
Figures
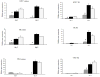
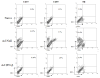
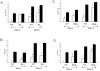
References
-
- Silverman RH. 2–5 A-dependent RNase L: a regulated endoribonuclease in the interferon system. In: Riordan GDAJF, editor. Ribonucleases: Structure and Function. Academic Press; New York: 1997. p. 515.
-
- Al-Khatib K, Williams BR, Silverman R, Halford WP, Carr DJ. The murine double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR and murine 2′, 5′-oligoadenylate synthetase-dependent RNase L are required for IFN-b-mediated resistance against herpes simplex virus type 1 in primary trigeminal ganglion culture. Virology. 2003;313:126. - PubMed
-
- Meurs E, Chong K, Galabru J, Thomas NS, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Hovanessian AG. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA- activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 1990;62:379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

