Urinary tract infection: is there a need for routine renal ultrasonography?
- PMID: 15102643
- PMCID: PMC1719898
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2002.019182
Urinary tract infection: is there a need for routine renal ultrasonography?
Abstract
Aims: To assess the yield of routine renal ultrasound (RUS) in the management of young children hospitalised with first uncomplicated febrile urinary tract infection (UTI).
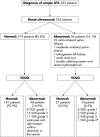
Methods: All children aged 0-5 years who had been hospitalised over a two year period with first uncomplicated febrile UTI in a medium size institutional regional medical centre were included. Children with known urinary abnormalities and/or who had been treated with antibacterial agents within seven days before admission were excluded. All included children underwent renal ultrasonography during hospitalisation and voiding cystouretrography (VCUG) within 2-6 months. The yield of RUS was measured by its ability to detect renal abnormalities, its sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for detecting vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), and by its impact on UTI management.
Results: Of 255 children that were included in the study, 33 children had mild to moderate renal pelvis dilatation on RUS suggesting VUR, of whom only nine had VUR on VCUG. On the other hand, in 36 children with VUR on VCUG the RUS was normal. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of abnormal RUS for detecting VUR were 17.7%, 87.6%, 23.5%, and 83.2% respectively. In none of the patients with abnormal RUS was a change in the management at or following hospitalisation needed.
Conclusion: Results show that the yield of RUS to the management of children with first uncomplicated UTI is questionable.
Figures
Comment in
-
Imaging guidelines for urinary tract infection in childhood; time for change?Arch Dis Child. 2004 May;89(5):398-9. doi: 10.1136/adc.2003.030734. Arch Dis Child. 2004. PMID: 15102621 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The value of renal ultrasound in children with a first episode of urinary tract infection.Ann Saudi Med. 2009 Jan-Feb;29(1):46-9. doi: 10.4103/0256-4947.51817. Ann Saudi Med. 2009. PMID: 19139618 Free PMC article.
-
Place of ultrasonography in predicting vesicoureteral reflux in patients with mild renal scarring.Urology. 2014 Apr;83(4):904-8. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.10.019. Epub 2013 Dec 7. Urology. 2014. PMID: 24315308
-
Role of Renal Ultrasonography in Predicting Vesicoureteral Reflux and Renal Scarring in Children Hospitalized with a First Febrile Urinary Tract Infection.Pediatr Neonatol. 2016 Apr;57(2):113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Pediatr Neonatol. 2016. PMID: 26163341
-
Vesicoureteral reflux and febrile urinary tract infections in anorectal malformations: a retrospective review.J Pediatr Surg. 2014 Jan;49(1):91-4; discussion 94. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.09.031. Epub 2013 Oct 5. J Pediatr Surg. 2014. PMID: 24439588 Review.
-
Dimercaptosuccinic acid scan challenges in childhood urinary tract infection, vesicoureteral reflux and renal scarring investigation and management.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2017 Apr;69(2):144-152. doi: 10.23736/S0393-2249.16.02509-1. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2017. PMID: 27355216 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating different imaging strategies in children after first febrile urinary tract infection.Pediatr Nephrol. 2010 Oct;25(10):2083-91. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1569-z. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20556431
-
Urinary tract infection in the newborn: clinical and radio imaging studies.Pediatr Nephrol. 2007 Oct;22(10):1735-41. doi: 10.1007/s00467-007-0556-5. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17665222
-
Increasing the Reliability of the Grading System for Voiding Cystourethrograms Using Ultrasonography: An Inter-Rater Comparison.Nephrourol Mon. 2016 Jul 31;8(5):e38685. doi: 10.5812/numonthly.38685. eCollection 2016 Sep. Nephrourol Mon. 2016. PMID: 27878111 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of renal anomalies after urinary tract infections in hospitalized infants less than 2 months of age.J Perinatol. 2010 Apr;30(4):281-5. doi: 10.1038/jp.2009.147. Epub 2009 Oct 8. J Perinatol. 2010. PMID: 19812586 Free PMC article.
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography for detection of renal damage in children.Pediatr Radiol. 2015 Jan;45(1):55-61. doi: 10.1007/s00247-014-3072-3. Epub 2014 Jul 27. Pediatr Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25064187 Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical