Inhibition of monocytic interleukin-12 production by Candida albicans via selective activation of ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 15102758
- PMCID: PMC387890
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.5.2513-2520.2004
Inhibition of monocytic interleukin-12 production by Candida albicans via selective activation of ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
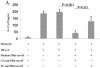
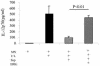
Our previous data demonstrated that live Candida albicans inhibits interleukin-12 (IL-12) production by human monocytes. Here we explored whether C. albicans inhibits IL-12 via a released factor and whether the inhibition is mediated via mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) regulation. Supernatant fluids were obtained from cultured C. albicans (SC5314) as well as cultured Saccharomyces cerevisiae after 20 h of incubation. At 2 h postincubation of monocytes with heat-killed C. albicans (HKCA) (2:1) to stimulate IL-12, concentrated fungal supernatant fluids were added and incubated for an additional 20 h. The present data show that, unlike supernatant fluids obtained from S. cerevisiae, the C. albicans supernatant fluids significantly suppressed IL-12 production induced by HKCA. This suggested that the inhibition is Candida specific. A preliminary biochemical analysis revealed that this secretory IL-12 inhibitory factor is glycoprotein in nature. The inhibitory activity had no effect on the phagocytosis of yeasts. Supernatant fluids from C. albicans markedly induced the phosphorylation of ERK44/42 MAPK, but not p38 and SAPK, 1 min after they were added to monocytes. To test if the induction of ERK44/42 MAPK was central to the IL-12 inhibition, we used gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) (1 ng/ml) plus lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (100 ng/ml) to stimulate IL-12 production by monocytes. The inhibition of ERK MAPK by the specific inhibitor PD 98059 significantly reduced phospho-ERK44/42 MAPK levels induced by C. albicans supernatant fluids in the IFN-gamma-plus-LPS-driven monocytes. Concomitantly, PD 98059 reversed the IL-12 inhibitory activity of the C. albicans supernatant (P < 0.01). These data indicate that C. albicans can inhibit IL-12 production by secreting an ERK44/42 MAPK-stimulating factor and thus can attenuate effective immune responses.
Figures


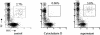

Similar articles
-
Characterization and partial purification of Candida albicans Secretory IL-12 Inhibitory Factor.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Feb 19;8:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-31. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18282300 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of monocyte-derived dendritic cell differentiation and interleukin-12 production by complement iC3b via a mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway.Exp Dermatol. 2005 Apr;14(4):303-10. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-6705.2005.00325.x. Exp Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 15810889
-
Alleviation of lipopolysaccharide-induced heart inflammation in poultry treated with carnosic acid via the NF-κB and MAPK pathways.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skae373. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae373. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 39657120
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recognition of non-self-polysaccharides by C-type lectin receptors dectin-1 and dectin-2.Glycobiology. 2009 Jun;19(6):568-75. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwp032. Epub 2009 Mar 14. Glycobiology. 2009. PMID: 19287024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Candida albicans with adherent human peripheral blood mononuclear cells increases C. albicans biofilm formation and results in differential expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines.Infect Immun. 2007 May;75(5):2612-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01841-06. Epub 2007 Mar 5. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17339351 Free PMC article.
-
PrtT-regulated proteins secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus activate MAPK signaling in exposed A549 lung cells leading to necrotic cell death.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 11;6(3):e17509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017509. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21412410 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Candida albicans and the mammalian innate host defense.Infect Immun. 2012 Apr;80(4):1304-13. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06146-11. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22252867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survival Strategies of Pathogenic Candida Species in Human Blood Show Independent and Specific Adaptations.mBio. 2020 Oct 6;11(5):e02435-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02435-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33024045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angulo, I., M. B. Jimenez-Diaz, J. F. Garcia-Bustos, D. Gargallo, F. G. de las Heras, M. A. Munoz-Fernandez, and M. Fresno. 2002. Candida albicans infection enhances immunosuppression induced by cyclophosphamide by selective priming of suppressive myeloid progenitors for NO production. Cell Immunol. 218:46-58. - PubMed
-
- Castro, M., J. A. Bjoraker, M. S. Rohrbach, and A. H. Limper. 1996. Candida albicans induces the release of inflammatory mediators from human peripheral blood monocytes. Inflammation 20:107-122. - PubMed
-
- Dong, C., R. J. Davis, and R. A. Flavell. 2002. MAP kinases in the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20:55-72. - PubMed
-
- Feng, G. J., H. S. Goodridge, M. M. Harnett, X. Q. Wei, A. V. Nikolaev, A. P. Higson, and F. Y. Liew. 1999. Extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases differentially regulate the lipopolysaccharide-mediated induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase and IL-12 in macrophages: Leishmania phosphoglycans subvert macrophage IL-12 production by targeting ERK MAP kinase. J. Immunol. 163:6403-6412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

