In vitro and in vivo characterization of Helicobacter hepaticus cytolethal distending toxin mutants
- PMID: 15102759
- PMCID: PMC387909
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.5.2521-2527.2004
In vitro and in vivo characterization of Helicobacter hepaticus cytolethal distending toxin mutants
Abstract
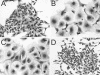
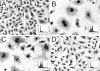
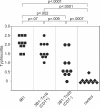
Helicobacter hepaticus expresses a member of the cytolethal distending toxin (CDT) family of bacterial cytotoxins. To investigate the role of CDT in the pathogenesis of H. hepaticus, transposon mutagenesis was used to generate a series of isogenic mutants in and around the cdtABC gene cluster. An H. hepaticus transposon mutant with a disrupted cdtABC coding region no longer produced CDT activity. Conversely, a transposon insertion outside of the cluster did not affect the CDT activity. An examination of these mutants demonstrated that CDT represents the previously described granulating cytotoxin in H. hepaticus. Challenge of C57BL/6 interleukin 10(-/-) mice with isogenic H. hepaticus mutants revealed that CDT expression is not required for colonization of the murine gut. However, a CDT-negative H. hepaticus mutant had a significantly diminished capacity to induce lesions in this murine model of inflammatory bowel disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of host immune responses by the cytolethal distending toxin of Helicobacter hepaticus.Infect Immun. 2006 Aug;74(8):4496-504. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00503-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16861635 Free PMC article.
-
Cytolethal distending toxin is essential for Helicobacter hepaticus colonization in outbred Swiss Webster mice.Infect Immun. 2005 Jun;73(6):3559-67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3559-3567.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15908385 Free PMC article.
-
Cytolethal distending toxin sequence and activity in the enterohepatic pathogen Helicobacter hepaticus.Infect Immun. 2000 Jan;68(1):184-91. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.184-191.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10603386 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter hepaticus infection in mice: models for understanding lower bowel inflammation and cancer.Mucosal Immunol. 2011 Jan;4(1):22-30. doi: 10.1038/mi.2010.61. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Mucosal Immunol. 2011. PMID: 20944559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter hepaticus, a new pathogenic species of the Helicobacter genus: Similarities and differences with H. pylori.Iran J Microbiol. 2013 Sep;5(3):185-94. Iran J Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24475322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The interplay between microbiome dynamics and pathogen dynamics in a murine model of Clostridium difficile Infection.Gut Microbes. 2011 May-Jun;2(3):145-58. doi: 10.4161/gmic.2.3.16333. Epub 2011 May 1. Gut Microbes. 2011. PMID: 21804357 Free PMC article.
-
Cytolethal distending toxin: a conserved bacterial genotoxin that blocks cell cycle progression, leading to apoptosis of a broad range of mammalian cell lineages.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Jul;157(Pt 7):1851-1875. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.049536-0. Epub 2011 May 12. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21565933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of acute diarrheal illness by persistent bacterial infection.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):4851-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00745-08. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18710857 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Cytolethal Distending Toxin-Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in a Glycogen Synthase Kinase (GSK)-3-Dependent Manner in Oral Keratinocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 5;23(19):11831. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911831. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233133 Free PMC article.
-
Role of bacteria in carcinogenesis, with special reference to carcinoma of the gallbladder.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov 21;16(43):5395-404. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5395. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21086555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avenaud, P., A. Marais, L. Monteiro, B. Le Bail, P. Bioulac Sage, C. Balabaud, and F. Megraud. 2000. Detection of Helicobacter species in the liver of patients with and without primary liver carcinoma. Cancer 89:1431-1439. - PubMed
-
- Burich, A., R. Hershberg, K. Waggie, W. Zeng, T. Brabb, G. Westrich, J. L. Viney, and L. Maggio-Price. 2001. Helicobacter-induced inflammatory bowel disease in IL-10- and T cell-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 281:G764-G778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

