In vivo activation of PPAR target genes by RXR homodimers
- PMID: 15103326
- PMCID: PMC424365
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600209
In vivo activation of PPAR target genes by RXR homodimers
Abstract
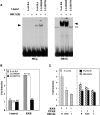
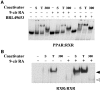
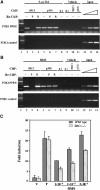
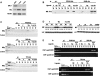
The ability of a retinoid X receptor (RXR) to heterodimerize with many nuclear receptors, including LXR, PPAR, NGF1B and RAR, underscores its pivotal role within the nuclear receptor superfamily. Among these heterodimers, PPAR:RXR is considered an important signalling mediator of both PPAR ligands, such as fatty acids, and 9-cis retinoic acid (9-cis RA), an RXR ligand. In contrast, the existence of an RXR/9-cis RA signalling pathway independent of PPAR or any other dimerization partner remains disputed. Using in vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation, we now show that RXR homodimers can selectively bind to functional PPREs and induce transactivation. At the molecular level, this pathway requires stabilization of the homodimer-DNA complexes through ligand-dependent interaction with the coactivator SRC1 or TIF2. This pathway operates both in the absence and in the presence of PPAR, as assessed in cells carrying inactivating mutations in PPAR genes and in wild-type cells. In addition, this signalling pathway via PPREs is fully functional and can rescue the severe hypothermia phenotype observed in fasted PPARalpha-/- mice. These observations have important pharmacological implications for the development of new rexinoid-based treatments.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide profiling of liver X receptor, retinoid X receptor, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α in mouse liver reveals extensive sharing of binding sites.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Feb;32(4):852-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06175-11. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22158963 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear import of the retinoid X receptor, the vitamin D receptor, and their mutual heterodimer.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 2;280(48):40152-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507708200. Epub 2005 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16204233
-
Effects of ligand binding on the association properties and conformation in solution of retinoic acid receptors RXR and RAR.J Mol Biol. 2001 Mar 23;307(2):557-76. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4409. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11254382
-
Modulation of RXR function through ligand design.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1821(1):57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.04.003. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21515403 Review.
-
[Retinoids: mechanisms of action].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2010 Nov;137 Suppl 3:S97-103. doi: 10.1016/S0151-9638(10)70036-3. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2010. PMID: 21185985 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Linseed oil supplementation affects fatty acid desaturase 2, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma, and insulin-like growth factor 1 gene expression in turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo).Anim Biosci. 2021 Apr;34(4):662-669. doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0030. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 32810939 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of transcription profile to reveal altered signaling pathways following the overexpression of human desumoylating isopeptidase 2 in pancreatic cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2016 Dec;12(6):4677-4684. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5298. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28105175 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of nongenomic activation of PI3K signalling by tetramerization of N-terminally-cleaved RXRα.Nat Commun. 2017 Jul 17;8:16066. doi: 10.1038/ncomms16066. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28714476 Free PMC article.
-
Histone hyperacetylation in the coding region of chromatin undergoing transcription in SV40 minichromosomes is a dynamic process regulated directly by the presence of RNA polymerase II.J Mol Biol. 2007 Jan 5;365(1):18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.044. Epub 2006 Sep 20. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17055528 Free PMC article.
-
M-ORBIS: mapping of molecular binding sites and surfaces.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(1):30-43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq736. Epub 2010 Sep 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20813758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger J, Leibowitz MD, Doebber TW, Elbrecht A, Zhang B, Zhou G, Biswas C, Cullinan CA, Hayes NS, Li Y, Tanen M, Ventre J, Wu MS, Berger GD, Mosley R, Marquis R, Santini C, Sahoo SP, Tolman RL, Smith RG, Moller DE (1999) Novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma and PPARdelta ligands produce distinct biological effects. J Biol Chem 274: 6718–6725 - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Wahli W (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev 20: 649–688 - PubMed
-
- Di-Poï N, Tan NS, Michalik L, Wahli W, Desvergne B (2002) Antiapoptotic role of PPARbeta in keratinocytes via transcriptional control of the Akt1 signaling pathway. Mol Cell 10: 721–733 - PubMed
-
- Dilworth FJ, Fromental-Ramain C, Remboutsika E, Benecke A, Chambon P (1999) Ligand-dependent activation of transcription in vitro by retinoic acid receptor alpha/retinoid X receptor alpha heterodimers that mimics transactivation by retinoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 1995–2000 - PMC - PubMed
-
- DiRenzo J, Soderstrom M, Kurokawa R, Ogliastro MH, Ricote M, Ingrey S, Horlein A, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK (1997) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and retinoic acid receptors differentially control the interactions of retinoid X receptor heterodimers with ligands, coactivators, and corepressors. Mol Cell Biol 17: 2166–2176 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

