Negative Staining and Image Classification - Powerful Tools in Modern Electron Microscopy
- PMID: 15103397
- PMCID: PMC389902
- DOI: 10.1251/bpo70
Negative Staining and Image Classification - Powerful Tools in Modern Electron Microscopy
Abstract
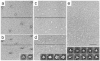
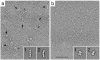
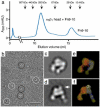
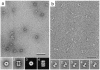
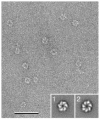
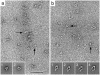
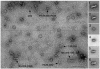
Vitrification is the state-of-the-art specimen preparation technique for molecular electron microscopy (EM) and therefore negative staining may appear to be an outdated approach. In this paper we illustrate the specific advantages of negative staining, ensuring that this technique will remain an important tool for the study of biological macromolecules. Due to the higher image contrast, much smaller molecules can be visualized by negative staining. Also, while molecules prepared by vitrification usually adopt random orientations in the amorphous ice layer, negative staining tends to induce preferred orientations of the molecules on the carbon support film. Combining negative staining with image classification techniques makes it possible to work with very heterogeneous molecule populations, which are difficult or even impossible to analyze using vitrified specimens.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cryo-negative staining.Micron. 1998 Apr-Jun;29(2-3):145-60. doi: 10.1016/s0968-4328(97)00068-1. Micron. 1998. PMID: 9684350
-
Cryo-negative staining reduces electron-beam sensitivity of vitrified biological particles.J Struct Biol. 2002 Jun;138(3):216-26. doi: 10.1016/s1047-8477(02)00035-7. J Struct Biol. 2002. PMID: 12217660
-
Structure of wet specimens in electron microscopy. Improved environmental chambers make it possible to examine wet specimens easily.Science. 1974 Nov 1;186(4162):407-14. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4162.407. Science. 1974. PMID: 4213401
-
Closer to the native state. Critical evaluation of cryo-techniques for Transmission Electron Microscopy: preparation of biological samples.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2014;52(1):1-17. doi: 10.5603/FHC.2014.0001. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2014. PMID: 24802956 Review.
-
Special specimen preparation methods for image processing in transmission electron microscopy: a review.J Microsc. 1978 Aug;113(3):241-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1978.tb00103.x. J Microsc. 1978. PMID: 361958 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial peroxiredoxin functions as crucial chaperone reservoir in Leishmania infantum.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 17;112(7):E616-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419682112. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25646478 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic mechanism for viral dsRNA length discrimination by MDA5 filaments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 4;109(49):E3340-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208618109. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23129641 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved arginine 380 of Hsp90 is not a catalytic residue, but stabilizes the closed conformation required for ATP hydrolysis.Protein Sci. 2012 Aug;21(8):1162-71. doi: 10.1002/pro.2103. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22653663 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Analysis of the Fusion and Attachment Glycoproteins of Mojiang Henipavirus.Viruses. 2021 Mar 22;13(3):517. doi: 10.3390/v13030517. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33809833 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of a ligand-free GPCR-Gαβγ intermediate complex.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 27:rs.3.rs-4566652. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4566652/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 38978591 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Radermacher M, Wagenknecht T, Verschoor A, Frank J. Three-dimensional reconstruction from a single-exposure, random conical tilt series applied to the 50S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J Microsc. 1987;146:113–136. - PubMed
-
- Adrian M, Dubochet J, Lepault J, McDowall AW. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature. 1984;308:32–36. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Zak O, Aisen P, Harrison SC, Walz T. Structure of the human transferrin receptor-transferrin complex. Cell. 2004;116:565–576. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

