Biophysical characterization of endotoxin inactivation by NK-2, an antimicrobial peptide derived from mammalian NK-lysin
- PMID: 15105110
- PMCID: PMC400566
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.5.1593-1599.2004
Biophysical characterization of endotoxin inactivation by NK-2, an antimicrobial peptide derived from mammalian NK-lysin
Abstract
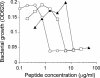
NK-2, a membrane-acting antimicrobial peptide, was derived from the cationic core region of porcine NK-lysin and consists of 27 amino acid residues. It adopts an amphipathic, alpha-helical secondary structure and has been shown to interact specifically with membranes of negatively charged lipids. We therefore investigated the interaction of NK-2 with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the main, highly anionic component of the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, by means of biophysical and biological assays. As model organisms and a source of LPS, we used Salmonella enterica strains with various lengths of the LPS carbohydrate moiety, including smooth LPS, rough LPS, and deep rough LPS (LPS Re) mutant strains. NK-2 binds to LPS Re with a high affinity and induces a change in the endotoxin-lipid A aggregate structure from a cubic or unilamellar structure to a multilamellar one. This structural change, in concert with a significant overcompensation of the negative charges of LPS, is thought to result in the neutralization of the endotoxic LPS activity in a cell culture system. Neutralization of LPS activity by NK-2 as well as its antibacterial activity against the various Salmonella strains strongly depends on the length of the sugar chains of LPS, with LPS Re being the most sensitive. This suggests that a hydrophobic peptide-LPS interaction is necessary for efficient neutralization of the biological activity of LPS and that the long carbohydrate chains, besides their function as a barrier for hydrophobic drugs, also serve as a trap for polycationic substances.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Molecular basis for endotoxin neutralization by amphipathic peptides derived from the alpha-helical cationic core-region of NK-lysin.Biophys Chem. 2010 Aug;150(1-3):80-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Biophys Chem. 2010. PMID: 20153101
-
Enhancement of endotoxin neutralization by coupling of a C12-alkyl chain to a lactoferricin-derived peptide.Biochem J. 2005 Jan 1;385(Pt 1):135-43. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041270. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15344905 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, activity and interactions of the cysteine deleted analog of tachyplesin-1 with lipopolysaccharide micelle: Mechanistic insights into outer-membrane permeabilization and endotoxin neutralization.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1818(7):1613-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.03.015. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22464970
-
Structural analysis of the NK-lysin-derived peptide NK-2 upon interaction with bacterial membrane mimetics consisting of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylglycerol.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2024 Mar;1866(3):184267. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2023.184267. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2024. PMID: 38159877 Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide (Endotoxin)-host defense antibacterial peptides interactions: role in bacterial resistance and prevention of sepsis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Sep;1758(9):1513-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.05.017. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16854372 Review.
Cited by
-
Simple and Rapid Endotoxin Recognition Using a Dipicolylamine-Modified Fluorescent Probe with Picomolar-Order Sensitivity.ACS Omega. 2022 Jul 15;7(29):25891-25897. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02935. eCollection 2022 Jul 26. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35910126 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical analysis of the interaction of granulysin-derived peptides with enterobacterial endotoxins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Oct;1768(10):2421-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.05.001. Epub 2007 May 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17555705 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli cell surface perturbation and disruption induced by antimicrobial peptides BP100 and pepR.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 3;285(36):27536-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130955. Epub 2010 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20566635 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature dependence of the binding of endotoxins to the polycationic peptides polymyxin B and its nonapeptide.Biophys J. 2005 Mar;88(3):1845-58. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.047944. Epub 2004 Dec 13. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15596502 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral and antibacterial peptides: Mechanisms of action.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 5;10(22):e40121. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40121. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39748995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersson, M., H. Gunne, B. Agerberth, A. Boman, T. Bergman, R. Sillard, H. Jörnvall, V. Mutt, B. Olsson, H. Wigzell, A. Dagerlind, H. G. Boman, and G. H. Gudmundsson. 1995. NK-lysin, a novel effector peptide of cytotoxic T and NK cells. Structure and cDNA cloning of the porcine form, induction by interleukin 2, antibacterial and antitumour activity. EMBO J. 14:1615-1625. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrä, J., and M. Leippe. 1999. Candidacidal activity of shortened synthetic analogs of amoebapores and NK-lysin. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 188:117-124. - PubMed
-
- Angus, D. C., W. T. Linde-Zwirble, J. Lidicker, G. Clermont, J. Carcillo, and M. R. Pinsky. 2001. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 29:1303-1310. - PubMed
-
- Blondelle, S. E., R. Jerala, M. Lamata, I. Moriyon, K. Brandenburg, J. Andrä, M. Porro, and K. Lohner. Structure-function studies of antimicrobial and endotoxin neutralizing peptides. In M. Chorev and T. K. Sawye (ed.), Peptide revolution: genomics, proteomics & therapeutics, in press. American Peptide Society, San Diego, Calif.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

