Membrane sphingolipid-ergosterol interactions are important determinants of multidrug resistance in Candida albicans
- PMID: 15105135
- PMCID: PMC400589
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.5.1778-1787.2004
Membrane sphingolipid-ergosterol interactions are important determinants of multidrug resistance in Candida albicans
Abstract
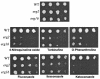
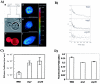
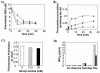
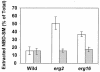
In this study, we examined the importance of membrane ergosterol and sphingolipids in the drug susceptibilities of Candida albicans. We used three independent methods to test the drug susceptibilities of erg mutant cells, which were defective in ergosterol biosynthesis. While spot and filter disk assays revealed that erg2 and erg16 mutant cells of C. albicans became hypersensitive to almost all of the drugs tested (i.e., 4-nitroquinoline oxide, terbinafine, o-phenanthroline, itraconazole, and ketoconazole), determination of the MIC at which 80% of the cells were inhibited revealed more than fourfold increase in susceptibility to ketoconazole and terbinafine. Treatment of wild-type C. albicans cells with fumonisin B1 resulted in 45% inhibition of sphingolipid biosynthesis and caused cells to become hypersensitive to the above drugs. Although erg mutants displayed enhanced membrane fluidity and passive diffusion, these changes alone were not sufficient to elicit the observed hypersusceptibility phenotype of erg mutants. For example, the induction in vitro of a 12% change in the membrane fluidity of C. albicans cells by a membrane fluidizer, benzyl alcohol, did not affect the drug susceptibilities of Candida cells. Additionally, the surface localization of green fluorescent protein-tagged Cdr1p, a major drug efflux pump protein of C. albicans, revealed that any disruption in ergosterol and sphingolipid interactions also interfered with its proper surface localization and functioning. A 50% reduction in the efflux of the Cdr1p substrate, rhodamine 6G, in erg mutant cells or in cells with a reduced sphingolipid content suggested a strong correlation between these membrane lipid components and this major efflux pump protein. Taken together, the results of our study demonstrate for the first time that there is an interaction between membrane ergosterol and sphingolipids, that a reduction in the content of either of these two components results in a disruption of this interaction, and that this disruption has deleterious effects on the drug susceptibilities of C. albicans cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional analysis of CaIPT1, a sphingolipid biosynthetic gene involved in multidrug resistance and morphogenesis of Candida albicans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Aug;49(8):3442-52. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3442-3452.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16048959 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane raft lipid constituents affect drug susceptibilities of Candida albicans.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Nov;33(Pt 5):1219-23. doi: 10.1042/BST20051219. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246085
-
Drug susceptibilities of yeast cells are affected by membrane lipid composition.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Dec;46(12):3695-705. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.12.3695-3705.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12435664 Free PMC article.
-
The synthesis, regulation, and functions of sterols in Candida albicans: Well-known but still lots to learn.Virulence. 2016 Aug 17;7(6):649-59. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1188236. Epub 2016 May 24. Virulence. 2016. PMID: 27221657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Sphingolipids in Amphotericin B Drug Resistance.Microb Drug Resist. 2023 Aug;29(8):319-332. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2022.0353. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Microb Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37327022 Review.
Cited by
-
Candida glabrata Transcription Factor Rpn4 Mediates Fluconazole Resistance through Regulation of Ergosterol Biosynthesis and Plasma Membrane Permeability.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Aug 20;64(9):e00554-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00554-20. Print 2020 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32571817 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of Candida albicans ABC Transporter Behavior in Real-Time via Fluorescence.Front Microbiol. 2015 Dec 9;6:1382. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01382. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26696990 Free PMC article.
-
Azole resistance in a Candida albicans mutant lacking the ABC transporter CDR6/ROA1 depends on TOR signaling.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 12;293(2):412-432. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.807032. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29158264 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role of farnesol in the modulation of Amphotericin B and Aureobasidin A antifungal drug susceptibility.Mycology. 2022 Oct 28;13(4):305-317. doi: 10.1080/21501203.2022.2138599. eCollection 2022. Mycology. 2022. PMID: 36405337 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of Fusarium oxysporum-Based Silver Nanoparticles on Candida spp. Oral Isolates.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;12(3):501. doi: 10.3390/nano12030501. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari, S., P. Gupta, S. K. Mahanty, and R. Prasad. 1993. The uptake of amino acids by erg mutants of Candida albicans. J. Med. Vet. Mycol. 31:377-386.
-
- Demeule, M., J. Jodoin, D. Gingras, and R. Beliveau. 2000. P-glycoprotein is localized in caveolae in resistant cells and in brain capillaries. FEBS Lett. 466:219-224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

