p19ARF determines the balance between normal cell proliferation rate and apoptosis during mammary gland development
- PMID: 15105443
- PMCID: PMC404024
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-11-0785
p19ARF determines the balance between normal cell proliferation rate and apoptosis during mammary gland development
Abstract
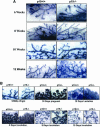
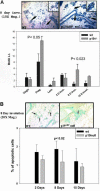
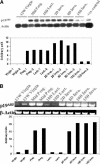
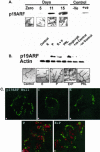
This study demonstrated, for the first time, the following events related to p19(ARF) involvement in mammary gland development: 1) Progesterone appears to regulate p19(ARF) in normal mammary gland during pregnancy. 2) p19(ARF) expression levels increased sixfold during pregnancy, and the protein level plateaus during lactation. 3) During involution, p19(ARF) protein level remained at high levels at 2 and 8 days of involution and then, declined sharply at day 15. Absence of p19(ARF) in mammary epithelial cells leads to two major changes, 1) a delay in the early phase of involution concomitant with downregulation of p21(Cip1) and decrease in apoptosis, and 2) p19(ARF) null cells are immortal in vivo measured by serial transplantion, which is partly attributed to complete absence of p21(Cip1) compared with WT cells. Although, p19(ARF) is dispensable in mammary alveologenesis, as evidenced by normal differentiation in the mammary gland of pregnant p19(ARF) null mice, the upregulation of p19(ARF) by progesterone in the WT cells and the weakness of p21(Cip1) in mammary epithelial cells lacking p19(ARF) strongly suggest that the functional role(s) of p19(ARF) in mammary gland development is critical to sustain normal cell proliferation rate during pregnancy and normal apoptosis in involution possibly through the p53-dependent pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
p19(ARF) is dispensable for oncogenic stress-induced p53-mediated apoptosis and tumor suppression in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(1):370-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.370-377.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11739748 Free PMC article.
-
p19Arf suppresses growth, progression, and metastasis of Hras-driven carcinomas through p53-dependent and -independent pathways.PLoS Biol. 2004 Aug;2(8):E242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020242. Epub 2004 Aug 17. PLoS Biol. 2004. PMID: 15314658 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of p19ARF enhances the defects of Mdm2 overexpression in the mammary gland.Oncogene. 2002 May 16;21(22):3525-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205441. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12032854
-
The role of Stat3 in apoptosis and mammary gland involution. Conditional deletion of Stat3.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;480:129-38. doi: 10.1007/0-306-46832-8_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000. PMID: 10959419 Review.
-
Regulation of apoptosis during mammary involution by the p53 tumor suppressor gene.J Dairy Sci. 2002 May;85(5):1103-10. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(02)74171-4. J Dairy Sci. 2002. PMID: 12086044 Review.
Cited by
-
Farnesoid X receptor functions in cervical cancer via the p14ARF-mouse double minute 2-p53 pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 May;49(5):3617-3625. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07201-x. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35347542 Free PMC article.
-
ARF: a versatile DNA damage response ally at the crossroads of development and tumorigenesis.Front Genet. 2014 Jul 22;5:236. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00236. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25101116 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Canonical Functions of the ARF Tumor Suppressor in Development and Tumorigenesis.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):86. doi: 10.3390/biom11010086. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33445626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of the p19(ARF) tumor suppressor affects intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and integrity.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Aug 15;104(6):2228-40. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21779. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18442038 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF6 maintains mammary stem cells and promotes pregnancy-induced mammary epithelial cell expansion.Commun Biol. 2019 Aug 6;2:292. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0547-7. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 31396572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cong, F., Zou, X., Hinrichs, K., Calame, K., and Goff, S.P. (1999). Inhibition of v-Abl transformation by p53 and p19ARF. Oncogene 18, 7731–7739. - PubMed
-
- Eymin, B., Karayan, L., Séité, P., Brambilla, C., Brambilla, E., Larsen, C.-J., and Gazzéri, S. (2001). Human ARF binds E2F1 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. Oncogene 20, 1033–1041. - PubMed
-
- Fruth, A.P. (1999). Mammary gland involution and apoptosis of mammary epithelial cells. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 4, 123–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

