Quetiapine for schizophrenia
- PMID: 15106155
- PMCID: PMC7032613
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000967.pub2
Quetiapine for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Quetiapine is an atypical antipsychotic with, theoretically, a low propensity for movement disorder adverse effects. It is used for the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychoses.
Objectives: To determine the effects of quetiapine for schizophrenia in comparison to placebo, and other antipsychotics.
Search strategy: Electronic searches of the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Register of Trials (February 2003), Biological Abstracts (1982-2000), CINAHL (1982-2000), the Cochrane Library (2000, Issue 1),EMBASE (1980-2000), MEDLINE (1966-2000), PsycLIT (1974-2000), SIGLE on CD (1980-1997), SocioFile (1974-1997) and many conference proceedings and hand searches of specific journals were undertaken. We contacted AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals for information regarding unpublished trials. The review was updated in February 2003.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials where adults with schizophrenia or similar illnesses were assigned to quetiapine, placebo or other neuroleptic drugs and where clinically relevant outcomes were reported.
Data collection and analysis: Citations and, where possible, abstracts were inspected independently by reviewers, papers ordered, re-inspected and quality assessed. We independently extracted data. We analysed data using fixed effects relative risk (RR) and estimated the 95% confidence interval (CI). Only homogeneous data were interpreted as favouring treatment or control. Where possible we calculated the number needed to treat (NNT) or number needed to harm statistics (NNH). We calculated relative risk (RR) for dichotomous data, and weighted mean differences (WMD) for continuous data.
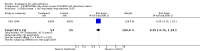
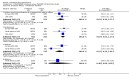
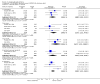
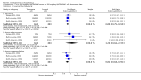
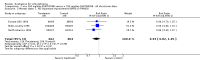
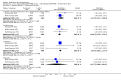
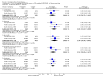
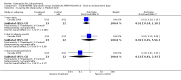
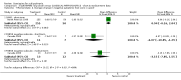
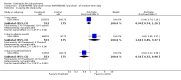
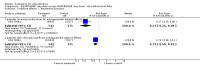
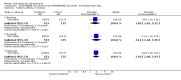
Main results: Despite the fact that 3443 people were randomised in 12 quetiapine studies, there are almost no data on service utilisation, economic outcomes, social functioning and quality of life. Over half of those within the quetiapine versus placebo comparison were lost to follow up (53% quetiapine vs 61% placebo, n=716, 4RCTs, RR 0.84 CI 0.7 to 0.9, NNT 11 CI 7 to 55) so it is impossible to interpret any ratings of global or mental state within this comparison with confidence. People allocated quetiapine, however, did not have more movement disorders than those given placebo (n=395, 2 RCTs, RR needing medication for EPSE 0.62 CI 0.3 to 1.2). The same applies to the comparison of >/= 250 mg/day quetiapine with < 250 mg/day quetiapine (49% dropout >/= 250 mg/day vs 58% < 250 mg/day, n=1066, 3 RCTs, RR 0.84 CI 0.8 to 0.9, NNT 11 CI 7 to 29). It should be noted that two deaths occurred in the higher dose group (n=618, 1 RCT, RR 0.1 CI 0.0 to 2.1). When quetiapine was compared with typical antipsychotics, about 36% of both groups failed to complete the short-term studies (n=1624, 6 RCTs, RR 0.87 CI 0.8 to 1.0). Average change in global state was heterogeneous and equivocal (n=762, 3 RCTs, WMD in short term 0.19 CI 0.00 to 0.38, I squared 76%). Mental state measures were also equivocal (n=1247, RR not improved 0.97 CI 0.9 to 1.1) including specific measures of negative symptoms (n=305, 1 RCT, MD change in SANS short term 0.94 CI -0.2 to 2.0). Movement disorders were less prevalent for those allocated quetiapine (n=1117, 4 RCTs, RR needing medication for extrapyramidal adverse effects 0.47 CI 0.4 to 0.6, NNT 4 CI 4 to 5, I squared 88%). Dry mouth (n=649, 2 RCTs, RR short term 2.85 CI 1.5 to 5.6, NNH 17 CI 7 to 65) and sleepiness (n=959, 3 RCTs, RR 1.51 CI 1.1 to 2.2, NNH 18 CI 8 to 181) may also be more prevalent for people given quetiapine compared with the older drugs. In the quetiapine versus risperidone comparison, over 30% of people left the study before completion (n=728, 1 RCT, RR 0.94 CI 0.7 to 1.2). Four people, all treated with quetiapine, died during the study (n=728, 1 RCT, RR 2.86 CI 0.2 to 52.8). Continuous mental state measures did not show clear differences between the two drugs (n=637, 1 RCT, MD PANSS 1.2 CI -2.0 to 4.4). However, considerably fewer people given quetiapine needed medication for extrapyramidal side effects compared with those allocated to risperidone (n=712, 1 RCT, RR 0.27 CI 0.2 to 0.5, NNT 11 CI 10 to 16). Quetiapine caused more dizziness (n=728, 1 RCT, RR 1.85 CI 1.0 to 3.3, NNH 18 CI 7 to 487), more dry mouth (n=728, 1 RCT, RR 2.11 CI 1.2 to 3.8, NNH 14 CI 6 to 82) and more sleepiness than risperidone (n=728, 1 RCT, RR 2.03 CI 1.4 to 2.9, NNH 7 CI 4 to 17).
Reviewers' conclusions: Quetiapine is effective for the treatment of schizophrenia, but it is not much different from first-generation antipsychotics and risperidone with respect to treatment withdrawal and efficacy. In comparison to first-generation antipsychotics and risperidone, quetiapine has a lower risk of movement disorders but higher risks of dizziness, dry mouth and sleepiness. More clearly reported pragmatic randomised controlled trials should be carried out to determine its position in everyday clinical practice. Studies of medium and long-term effects, including cost-effectiveness, quality of life, social functioning and service utilisation, in comparison with the effects of typical and atypical antipsychotics should be priority areas.
Conflict of interest statement
In the past five years Manit Srisurapanont has received honoraria and support for attending national and international scientific meetings from AstraZeneca (Thailand), Eli Lilly Asia, Inc. (Thailand), GlaxoSmithKline (Thailand), Janssen‐Cilag (Thailand), Servier (Thailand) and Solvay Pharmaceuticals (Thailand). Narong Maneeton and Benjaluk Maneeton have received similar support for attending national scientific meetings from GlaxoSmithKline (Thailand) and Janssen‐Cilag (Thailand).
Figures























Update of
-
Quetiapine for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(3):CD000967. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000967. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD000967. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000967.pub2. PMID: 10908478 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Africa‐Europe 1994 {published data only}
-
- Link C, Smith A, Miller B, Ryan J. A multicentre, double‐blind, controlled comparison of 'Seroquel' and chlorpromazine in acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. 1994 International Conference on Schizophrenia, Vancouver, BC, Canada. Aug 21‐24, 1994.
-
- Link C, Smith A, Miller B, Ryan J, Study Group. A multicentre, double‐blind, controlled comparison of 'Seroquel' and chlorpromazine in the treatment of hospitalised patients with acute exacerbation of subchronic and chronic schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 1994; Vol. 4:385.
-
- Peuskens J, Link CGG. A comparison of quetiapine and chlorpromazine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1997;96:265‐73. - PubMed
Canada 2000 {unpublished data only}
-
- Purdon S, Malla A, Labelle A, Litt W. Long‐term treatment of quetiapine improves cognitive function in schizophrenia: a double‐blind study. Schizophrenia Winter Workshop, Davos, Switzerland 2000.
Europe‐USA 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hirsch S, Arvanitis L, Miller B, Smith A, Study Group. A multicentre, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled comparison of low and high dosage regimens of 'Seroquel' in the treatment of hospitalised patients with acute exacerbation of subchronic or chronic schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1994;4:384‐5.
-
- Link CGG, Arvanitis L, Study Group. 'Seroquel' treatment of hospitalised patients with acute exacerbation of subchronic or chronic schizophrenia. A multicentre, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind comparison of low and high dosage regimens. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1995;5:346‐7.
-
- Small JG, Hirsch SR, Arvanitis LA, Miller BG, Link CGG, the Seroquel Study Group. Quetiapine in patients with schizophrenia. A high‐ and low‐dose double‐blind comparison with placebo. Archives of General Psychiatry 1997;54:549‐57. - PubMed
Japan 1999a {unpublished data only}
-
- Kudo Y, Nomura J, Ikawa G, Nakajima T, Saito M, Sakai T, Yoshimasu F, Hanada M, Kuroda S, Watanabe M, Yamawaki S, Tashiro N, Nakane Y, Tanaka M. Clinical evaluation of quetiapine fumarate for the treatment of schizophrenia: a double‐blind controlled study using mosapramine hydrochloride as a control. Rinsyo Iyaku 2000;16(12):1807‐42.
-
- Kudo Y, Nomura J, Ikawa G, Nakajima T, Saito M, Sakai T, Yoshimasu F, Hanada M, Kuroda S, Watanabe S, Yamawaki S, Tahiro N, Nakame Y, Tanaka M, on behalf of the ICI 204 636 clinical evaluation group. Clinical trial of quetiapine in schizophrenia ‐ efficacy and tolerability of quetiapine: a comparative double‐blind study with masopramine in schizophrenic patients. 1999 Annual Meeting of the World Psychiatric Association, Hamburg, Germany 1999.
Japan 1999b {unpublished data only}
-
- Inada T, Marasaki M. The drug‐induced extrapyramidal symptoms scale: differentiation of extrapyramidal symptom profiles and identification of favourable extrapyramidal symptom profile of quetiapine in Japanese patients. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 2001; Vol. 11 (Suppl 3):S265.
-
- Murasaki M, Koyama T, Yamauchi T, Yagi MG, Ushijima S, Kamijima K. Clinical evaluation of quetiapine in schizophrenia ‐ efficacy and tolerability of quetiapine compared with haloperidol in patients with schizophrenia. 1999 Annual Meeting of the World Psychiatric Association 1999.
Multi‐country 1995 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Barzega G, Bogetto F, Maina G, Ravizza L. [Efficacia e tollerabilita dell' antipsychotico atipico quetiapina: uno studio in doppio cieco]. Minerva Psichiatrica 1999;40:297‐305.
-
- Barzega G, Bogetto F, Maina G, Ravizza L. Quetiapine in schizophrenic patients: a high‐ and low‐dose double‐blind comparison. European Journal of Psychiatry 2000;14(4):221‐32.
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Link CCG, Horne B. A multicentre, double‐blind, randomised comparison of dose and dose regimen of 'Seroquel' in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. 34th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, San Juan, Puerto Rico. Dec 11‐15, 1995.
-
- King DJ, Link CGC. 'Seroquel' (ICI 204636): an atypical antipsychotic ‐ results from Phase III. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1996;6(Suppl 3):202.
-
- King DJ, Link CGG. Seroquel (ICI 204636): an atypical antipsychotic results from Phase III. XXth Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum, Melbourne, Australia. June 23‐27, 1996.
Multi‐country 1996 {unpublished data only}
-
- Copolov DL, Link CGG, Kowalcyk B. A multicentre, double‐blind, randomized comparison of quetiapine (ICI 204,636, 'Seroquel') and haloperidol in schizophrenia. Psychological Medicine 2000;30(1):95‐106. - PubMed
-
- Fleishhacker W, Link C, Hurst B. ICI 204,636 (Seroquel) ‐ a putative new antipsychotic: results from Phase III trials. Schizophrenia Research 1996;18:32.
-
- Hellewell JSE, Hurst BC, Link CGG. Switching from a conventional antipsychotic (haloperidol) to an atypical antipsychotic ('Seroquel'‐ICI 204,636). European Neuropsychopharmacology 1996;6(Suppl 4):123.
-
- Link C, Farrow L. 'Seroquel'™ (ICI 204, 636) EPS and prolactin ‐ comparison with haloperidol. 10th World Congress of Psychiatry, Madrid, Spain. Aug 23‐28, 1996.
-
- Zeneca Pharmaceuticals. Data on file supporting the claims: study 0014 (quetiapine vs haloperidol).
Multi‐country 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Buckley PF, Goldstein JM, Emsley RA. Comparison of quetiapine and haloperidol in treatment‐resistant schizophrenia. Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5‐10; LA, USA. 2001.
-
- Emsley RA, Bailey P, Jones AM, Raniwalla JTI. Efficacy of quetiapine fumarate in partial responders. 1999 Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatry Association, Washington, DC, USA. 1999.
-
- Emsley RA, Jones AM. Treatment of depressive symptoms in partially refractory schizophrenia: efficacy of quetiapine versus haloperidol. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2001;11(3):S264.
-
- Emsley RA, Raniwalla J, Bailey P, Jones AM. [Efficacy and tolerability of 'Seroquel' compared with haloperidol in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to conventional antipsychotic treatment]. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999; Vol. 9, issue Suppl 5:S267.
-
- Emsley RA, Raniwalla J, Bailey P, Jones AM. Efficacy and tolerability of 'Seroquel' compared with haloperidol in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to conventional antipsychotic treatment. 1999 Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, London, UK. 1999.
North America 1996 {published data only}
-
- Addington DE, Arvanitis LA. 'Seroquel' (quetiapine): an atypical antipsychotic ‐ results from a multiple fixed dose, placebo‐controlled study. Schizophrenia 1996 ‐ Breaking Down the Barriers, 4th International Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada. Oct 6‐9, 1996.
-
- Arvanitis LA, Miller BG. 'Seroquel' (ICI 204,636): an atypical antipsychotic: results from a multiple fixed dose, placebo‐controlled study. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1996;6(Suppl 3):148.
-
- Arvanitis LA, Miller BG. Quetiapine, an atypical antipsychotic ‐ results from a multiple fixed dose, placebo‐controlled study. 149th Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association, New York, NY, USA. May 4‐9, 1996.
-
- Arvanitis LA, Miller BG and Study Group. ICI 204,636, an atypical antipsychotic: results from a multiple fixed‐dose, placebo‐controlled trial. Pyschopharmacology Bulletin 1966;32:391.
-
- Arvanitis LA, Miller BG, Kowalcyk BB. Efficacy of 'Seroquel' (Quetiapine Fumarate) in affective symptoms of schizophrenia. 36th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 1997.
USA 1990 {published data only}
-
- Fabre L, Slotnick V, Jones V, Murray G, Malick J. ICI 204,636, a novel atypical antipsychotic: early indication for safety and efficacy in man. 17th Congress of Collegium International Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum, Kyoto, Japan. Sep 10‐14, 1990.
-
- Fabre LF, Arvanitis L, Pultz J, Jones VM, Malick JB, Slotnick VB. ICI 204,636, a novel, atypical antipsychotic ‐ early indication of safety and efficacy in patients with chronic and subchronic schizophrenia. Clinical Therapeutics 1995;17:366‐78. - PubMed
USA 1994 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Borison RL, Arvanitis LA, Miller BG, Study Group. ICI 204,636, an atypical antipsychotic ‐ efficacy and safety in a multicenter, placebo‐controlled trial in patients with schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1996;16:158‐69. - PubMed
-
- Link C, Arvanitis L, Miller B, Fennimore J, Study Group. A multicentre, placebo‐controlled double‐blind evaluation of 'Seroquel' in hospitalised patients with acute exacerbation of chronic and subchronic schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1994;4:385‐6.
-
- Link CGG, Arvanitis L, Study Group. 'Seroquel' treatment of hospitalised patients with acute exacerbation of chronic and subchronic schizophrenia. A multicentre, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1995;5:346.
USA 2000a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mullen J. A health economic evaluation of quetiapine compared with risperidone: a supplement analysis of the QUEST Trial. 39th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2000 Dec 10‐14; San Juan; Puerto Rico. 2000.
-
- Mullen J. Health economic evaluation of quetiapine and risperidone in the QUEST Trial. Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5‐10; LA, USA. 2001.
-
- Mullen J, Jibson JD, Sweitzer D, for the QUEST Study Group. A comparison of the relative safety, efficacy, and tolerability of quetiapine and risperidone in outpatients with schizohrenia and other psychotic disorders: the quetiapine experience with safety and tolerability (QUEST) study. Clinical Therapeutics 2001;23:1839‐54. - PubMed
-
- Tandon R. Quetiapine and risperidone in outpatients with schizophrenia: subanalysis of the QUEST Trial. 7th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry; 2001 Jul 1‐6; Berlin, Germany. 2001.
-
- Tandon R. Quetiapine and risperidone in outpatients with schizophrenia: subanalysis of the QUEST trial. Annuan Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5‐10; LA, USA. 2001.
References to studies excluded from this review
Faustman 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Faustman WO, Ringo DL, Lauriello J, Lim KO, Pfefferbaum A. Effects of 'Seroquel' (quetiapine) on platelet serotonin‐2 binding in schizophrenia [letter]. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1996;16:464‐6. - PubMed
-
- Faustman WO, Ringo DL, Lauriello J, Lim KO, Pfefferbaum A, Bardgett ME, et al. Effects of 'Seroquel' (ICI 204,636) on platelet serotonin‐2 binding in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1995;15:149. - PubMed
Gefvert 1995 (029) {published data only}
-
- Gefvert O, Lindström LH, Langström B, Bergström M, Lundberg T, Yates RA. Time course for dopamine and serotonin receptor occupancy in the brain of schizophrenic patients following dosing with 150 mg 'Seroquel' tid. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1996;6(Suppl 3):74.
-
- Gefvert O, Lindström LH, Langström B, Bergström M, Lundberg T, Yates RA. Time course for dopamine and serotonin receptor occupancy in the brain of schizophrenic patients following dosing with 150 mg 'Seroquel' tid. Schizophrenia Research 1996;18:139‐40.
-
- Gefvert O, Lindström LH, Langström B, Bergström M, Lundberg T, Yates RA, Larsson SD, Tuersley MD. Time course for dopamine and serotonin receptor occupancy in the brain of schizophrenic patients following dosing with 150 mg 'Seroquel' (ICI 204,636) tid. 34th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, San Juan, Puerto Rico. Dec 11‐15, 1995.
-
- Gefvert O, Lindström LH, Langström B, Bergström M, Lundberg T, Yates RA, Larsson SD, Tuersley MD. Time course of dopamine and serotonin receptor occupancy in the brain of schizophrenic patients following dosing with 150 mg 'Seroquel' tid. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1995;5:347.
Kufferle 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kufferle B, Tauscher J, Asenbaum S, Vesely C, Podreka I, Bruke T, Kasper S. IBZM SPECT imaging of striatal dopamine‐2 receptors in psychotic patients treated with the novel antipsychotic substance quetiapine in comparison to clozapine and haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 1997;133:323‐8. - PubMed
Shimada 1994 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Shimada E, Murasaki M, Miura S, Sadakuni F, Yoshimoto W. A Phase I study in healthy volunteers of ICI 204,636, a novel neuroleptic agent. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 1994;72(Suppl 1):445.
Tauscher 1997 {published data only}
-
- Tauscher J, Kufferle B, Asenbaum S, Brucke T, Kasper S. Previous treatment as a confounding variable in studies with novel antipsychotics: two cases of high dopamine‐2 receptor occupancy with quetiapine. Psychopharmacology 1997;133:102‐5. - PubMed
Thyrum 1996 (017) {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Thyrum PT, Jaskiw G, Fuller M, Wongs JYW, Ewing BJ, Yeh C. Multiple‐dose pharmacokinetics of ICI 204,636 in elderly patients with selected psychotic disorders. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1996;32:524.
Wetzel 1995 (005) {published data only}
-
- Benkert O, Wetzel H, Hillert A. Does 5‐HT2 blockade contribute to the effect of antipsychotic drugs? Focus on risperidone and 'Seroquel'. European Psychiatry 1994;9(Suppl1):53S.
-
- Fabre LF. A multicenter, open trial of ICI 204,636 in hospitalized patients with acute psychotic symptomatology. Schizophrenia Research 1993;9:273.
-
- Hain C, Schlegel S, Szegedi A, Wetzel H. Topographic EEG analysis in schizophrenic patients treated with ICI 204636, a new dibenzothiazepine with atypical antipsychotic properties. Pharmacopsychiatry 1993;26:156.
-
- Szegedi A, Wiesner J, Hillert A, Hammes E, Wetzel H, Benkert O. ICI 204636, a putative "atypical" antipsychotic, in the treatment of schizophrenia with positive symptomatology: an open clinical trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 1993;26:197.
-
- Wetzel H, Szegedi A, Hain C, Wiesner J, Schlegel S, Benkert O. Seroquel (ICI 204 636), a putative "atypical" antipsychotic, in schizophrenia with positive symptomatology: results of an open clinical trial and changes of neuroendocrinological and EEG parameters. Psychopharmacology 1995;119:231‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Germany 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Lambert M, Mortiz S, Karow A, Krausz M, Naber D. Quality of life in the treatment of schizophrenia ‐ a randomized, open‐label comparison trial of amisulpride, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone and zotepine. Schizophrenia Research 2002;53(3 Suppl 1):176.
Italy 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Mauri MC, Steinhilber CPC, Laini V, Pavone F, Barale F. Olanzapine and quetiapine in the treatment of acute schizophrenia: a descriptive analysis. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;5(Suppl 1):S119.
Japan 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Mori K, Nagao M, Yamashita H, Yamawaki S. Effects of switching to atypical antipsychotics on memory in chronic schizophrenic patients. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002; Vol. 5, issue Suppl 1:S80.
-
- Nagao M, Mori K, Yamashita H, Yamawaki S. Switching to typical antipsychotics in chronic schizophrenic patients: prediction factors of efficacy. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;5(Suppl 1):S123.
Netherlands 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bruggeman R, Knegtering H, Castelein S, Linde J, Bous J. Risperidone versus quetiapine: preliminary results of a comparative study on sexual dysfunctioning and prolactin elevation. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 2002;56(2):14‐5.
Turkey 2001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Atmaca M, Kuloglu M, Tezcan E, Gecici O, Unal A, Firidin B. The comparison of quetiapine and haloperidol effects on serum prolactin in patients with schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2001;11(Suppl 3):S240.
USA 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Velligan DI. Neurocognitive advantages of quetiapine. Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, LA, USA. 2001.
-
- Velligan DI, Pultz J, Csernansky JG, Hoff AL, Mahurin R, Miller AL, Newcommer JW. Changes in cognitive function in quetiapine fumarate versus haloperidol. 1999 American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA. 1999.
USA 2001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Lee M, Meltzer HY. Quetiapine is significantly superior to haloperidol and placebo in improving mood in patients with schizophrenia. 7th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry; 2001 Jul 1‐6; Berlin, Germany. 2001.
References to ongoing studies
UK 2003 {unpublished data only}
-
- Personal communication. Anonymous 2003.
USA 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hong WW, Rak IW, Ciuryla VT, Wilson AM, Kylstra JW, Meltzer HY, Carpenter Jr WT, Lehman A, Arvanitis LA. Medical‐claims databases in the design of a health‐outcomes comparison of quetiapine ('Seroquel') and usual‐care antipsychotic medication. Schizophrenia Research 1998;32:51‐8. - PubMed
USA 2000b {unpublished data only}
-
- Lieberman J, McEnvoy J, Stroup S. Protocol: comparative effectiveness of antipsychotic medications in patients with schizophrenia: revised in response to DSMB comments. National Institute of Mental Health 2000.
-
- Lieberman J, McEvoy J, Stroup S. Trial design summary: comparative effectiveness of antipsychotic medications in patients with schizophrenia: Draft. National Institute of Mental Health 2002.
-
- Lieberman JA, Schneider LS, McEvoy J, Pariot P, Stroup S, Adiao J, Lebowitz BD. Effectiveness trials of antipsychotic drugs. Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatry Association; 2001 May 5‐10; LA, USA.. 2001.
Additional references
Altman 1996
Andreasen 1984
-
- Andreasen NC. Scale for the assessment of negative symptoms (SANS). Iowa City: University of Iowa, 1984.
Barnes 1989
-
- Barnes TR. A rating scale for drug‐induced akathisia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1989;154:672‐6. - PubMed
Clarke 2002
-
- Clarke M, Oxman AD. The Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook. The Cochrane Library. Oxford: Update Software, 2002, issue 2.
Cook 1993
-
- Cook DJ, Guyatt GH, Ryan G, Clifton J, Buckingham L, Willan A, McIlroy W, Oxman AO. Should unpublished data be included in meta‐analyses?. JAMA 1993;269:2749‐53. - PubMed
Duggan 1999
-
- Duggan L, Fenton M, Dardennes RM, El‐Dosoky A, Indran S. Olanzapine for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1999, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001359] - DOI
Gilbody 2000
Goldstein 1993
-
- Goldstein JM, Litwin LC, Sutton EM, Malick JB. Seroquel: electrophysiological profile of a potential atypical antipsychotic. Psychopharmacology 1993;112:293‐8. - PubMed
Goldstein 1995
-
- Goldstein JM. Preclinical tests that predict clozapine‐like atypical antipsychotic actions. In: Brunello N, Racagni G, Langer SZ, Mendlewicz J editor(s). Critical issues in the treatment of schizophrenia. International Academy of Biomedical Drug Research. Vol. 10, Basel: Darger, 1995:95‐101.
Green 2003
-
- Green AI, Canuso CM, Brenner MJ, Wojcik JD. Detection and management of comorbidity in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatric Clinic of North America 2003;26:115‐39. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy Q. ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Publication ADM 76‐338. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health, Education and Welfare, 1976.
Hardon 1996
-
- Hardon DC, Baker D, Hodges JS, Hicks N. Rating the quality of evidence for clinical practice guidelines. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1996;49:749‐54. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Hirsch 1996
-
- Hirsch SR, Link CGG, Goldstein JM, Arvanitis LA. ICI 204,636: a new atypical antipsychotic drug. British Journal of Psychiatry 1996;168(Suppl 29):45‐56. - PubMed
Hunter 2003
Kane 1988
-
- Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer HY. Clozapine for the treatment‐resistant schizophrenia: a double‐blind comparison with chlorpromazine/benztropine. Archives of General Psychiatry 1988;45:789‐96. - PubMed
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Kerwin 1994
-
- Kerwin RW. The new atypical antipsychotics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1994;164:141‐8. - PubMed
Leucht 2003
Migler 1993
-
- Migler BM, Warawa EJ, Malick JB. Seroquel: behavioral profile of a potential atypical antipsychotic. Psychopharmacology 1993;112:299‐307. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987‐91. - PubMed
NICE 2002
-
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Guidance on the use of newer (atypical) antipsychotic drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia. NICE Technology Appraisal Guidance 2002; Vol. 43:1‐21.
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Peduzzi 2002
-
- Peduzzi P, Henderson W, Hartigan P, Lavori P. Analysis of randomized controlled trial. Epidemiological reviews 2002;24:26‐38. - PubMed
Roland 1998
Rummel 2003
Saller 1993
-
- Saller CF, Salama AI. Seroquel: biochemical profile of a potential atypical antipsychotic. Psychopharmacology 1993;112:285‐92. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson GM, Angus JW. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1970;Suppl 212:11‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

