Runx2 and Runx3 are essential for chondrocyte maturation, and Runx2 regulates limb growth through induction of Indian hedgehog
- PMID: 15107406
- PMCID: PMC395853
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1174704
Runx2 and Runx3 are essential for chondrocyte maturation, and Runx2 regulates limb growth through induction of Indian hedgehog
Abstract
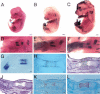
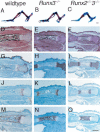
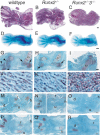
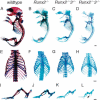
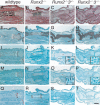
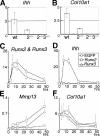
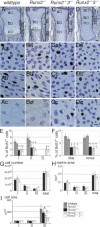
The differentiation of mesenchymal cells into chondrocytes and chondrocyte proliferation and maturation are fundamental steps in skeletal development. Runx2 is essential for osteoblast differentiation and is involved in chondrocyte maturation. Although chondrocyte maturation is delayed in Runx2-deficient (Runx2(-/-)) mice, terminal differentiation of chondrocytes does occur, indicating that additional factors are involved in chondrocyte maturation. We investigated the involvement of Runx3 in chondrocyte differentiation by generating Runx2-and-Runx3-deficient (Runx2(-/-)3(-/-)) mice. We found that chondrocyte differentiation was inhibited depending on the dosages of Runx2 and Runx3, and Runx2(-/-)3(-/-) mice showed a complete absence of chondrocyte maturation. Further, the length of the limbs was reduced depending on the dosages of Runx2 and Runx3, due to reduced and disorganized chondrocyte proliferation and reduced cell size in the diaphyses. Runx2(-/-)3(-/-) mice did not express Ihh, which regulates chondrocyte proliferation and maturation. Adenoviral introduction of Runx2 in Runx2(-/-) chondrocyte cultures strongly induced Ihh expression. Moreover, Runx2 directly bound to the promoter region of the Ihh gene and strongly induced expression of the reporter gene driven by the Ihh promoter. These findings demonstrate that Runx2 and Runx3 are essential for chondrocyte maturation and that Runx2 regulates limb growth by organizing chondrocyte maturation and proliferation through the induction of Ihh expression.
Figures

References
-
- Bae, S.C., Takahashi, E., Zhang, Y.W., Ogawa, E., Shigesada, K., Namba, Y., Satake, M., and Ito, Y. 1995. Cloning, mapping and expression of PEBP2 αC, a third gene encoding the mammalian Runt domain. Gene 159: 245–248. - PubMed
-
- Bi, W., Deng, J.M., Zhang, Z., Behringer, R.R., and de Crombrugghe, B. 1999. Sox9 is required for cartilage formation. Nat. Genet. 22: 85–89. - PubMed
-
- Bitgood, M.J. and McMahon, A.P. 1995. Hedgehog and Bmp genes are coexpressed at many diverse sites of cell–cell interaction in the mouse embryo. Dev. Biol. 172: 126–138. - PubMed
-
- Enomoto, H., Enomoto-Iwamoto, M., Iwamoto, M., Nomura, S., Himeno, M., Kitamura, Y., Kishimoto, T., and Komori, T. 2000. Cbfa1 is a positive regulatory factor in chondrocyte maturation. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 8695–8702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
