Antibiotic selection pressure and resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes
- PMID: 15109426
- PMCID: PMC3322805
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1003.030252
Antibiotic selection pressure and resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes
Abstract
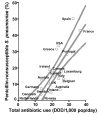
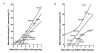
We correlated outpatient antibiotic use with prevalence of penicillin-nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae (PNSP), macrolide-resistant S. pneumoniae (MRSP), and macrolide-resistant S. pyogenes (MRGAS) in 20 countries. Total antibiotic use was correlated with PNSP (r = 0.75; p < 0.001), as was macrolide use with MRSP (r = 0.88; p < 0.001) and MRGAS (r = 0.71; p = 0.004). Streptococcal resistance is directly associated with antibiotic selection pressure on a national level.
Figures
References
-
- McGowan JE Jr. Antimicrobial resistance in hospital organisms and its relation to antibiotic use. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5:1033–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
