Cyclophilin A as a novel biphasic mediator of endothelial activation and dysfunction
- PMID: 15111303
- PMCID: PMC1615642
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63715-7
Cyclophilin A as a novel biphasic mediator of endothelial activation and dysfunction
Abstract
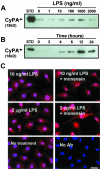
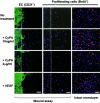
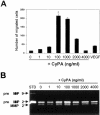
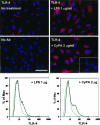
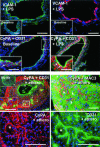
Inflammation-mediated endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction likely contributes to the pathogenesis of several vascular diseases including atherosclerosis. We found that stimulation of human umbilical vein ECs with lipopolysaccharide induced secretion of cyclophilin (CyPA) an intracellular protein belonging to the immunophilin family. We then found that when added exogenously CyPA has direct effects on ECs in vitro. At low concentrations (10 to 100 ng/ml) CyPA increased EC proliferation, migration, invasive capacity, and tubulogenesis. Gelatin zymography indicated increased secretion of active matrix metalloproteinase-2, a mediator of cell migration and angiogenesis. At high concentrations (eg, 2 microg/ml) CyPA had opposite effects, decreasing EC migration and viability, possibly in relation to induction of Toll-like receptor-4 expression, detected by immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry. In vivo CyPA expression was not detectable in the luminal ECs of normal mouse carotid arteries but was rapidly induced after systemic lipopolysaccharide injection. In an experimental mouse model of atherosclerosis, CyPA expression was detected in the ECs of neocapillaries of carotid artery lesions, supporting its association with pathological angiogenesis suggested by our in vitro results. In conclusion, we found that CyPA has a biphasic activity on ECs in vitro and is up-regulated in vivo in ECs under pathological states. Our results suggest that CyPA is a novel paracrine and autocrine modulator of EC functions in immune-mediated vascular disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cyclophilin A is a proinflammatory cytokine that activates endothelial cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004 Jul;24(7):1186-91. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000130664.51010.28. Epub 2004 May 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15130913
-
Cyclophilin A differentially activates monocytes and endothelial cells: role of purity, activity, and endotoxin contamination in commercial preparations.Atherosclerosis. 2008 Apr;197(2):564-71. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2007.08.025. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Atherosclerosis. 2008. PMID: 17919644
-
Cyclophilin A-FoxO1 signaling pathway in endothelial cell apoptosis.Cell Signal. 2019 Sep;61:57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.04.014. Epub 2019 May 4. Cell Signal. 2019. PMID: 31063815
-
Cyclophilin A in cardiovascular homeostasis and diseases.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2015 Jan;235(1):1-15. doi: 10.1620/tjem.235.1. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25743766 Review.
-
Cyclophilin A: a key player for human disease.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Oct 31;4(10):e888. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.410. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24176846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Induces Inflammatory Cytokines via Cyclophilin A-CD147 Activating the ERK-NF-κB Pathway in Human Urothelial Cells.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 9;11:2052. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02052. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013867 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cyclophilin A from brains of prion-infected mice in stimulation of cytokine release by microglia and astroglia in vitro.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 10;287(7):4628-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.269480. Epub 2011 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22179611 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer EMMPRIN (CD147) in Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 8;19(2):507. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020507. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29419744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro and in vivo validation of the antiviral effect of hCypA against SARS-CoV-2 via binding to the RBD of spike protein.Mol Ther. 2024 Jun 5;32(6):1805-1816. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.03.029. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38532628 Free PMC article.
-
Potential implications of Apolipoprotein E in early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage: Involvement in the modulation of blood-brain barrier integrity.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 30;7(35):56030-56044. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10821. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27463015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansson GK, Libby P, Schonbeck U, Yan ZQ. Innate and adaptive immunity in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2002;91:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Ostos MA, Recalde D, Zakin MM, Scott-Algara D. Implication of natural killer T cells in atherosclerosis development during a LPS-induced chronic inflammation. FEBS Lett. 2002;519:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Nakagomi A, Freedman SB, Geczy CL. Interferon-gamma and lipopolysaccharide potentiate monocyte tissue factor induction by C-reactive protein: relationship with age, sex, and hormone replacement treatment. Circulation. 2000;101:1785–1791. - PubMed
-
- Galat A. Peptidylproline cis-trans-isomerases: immunophilins. Eur J Biochem. 1993;216:689–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

