Size effects on diffusion processes within agarose gels
- PMID: 15111390
- PMCID: PMC1304142
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74325-8
Size effects on diffusion processes within agarose gels
Abstract
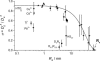
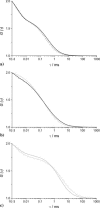
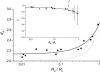
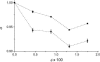
To investigate diffusion processes in agarose gel, nanoparticles with sizes in the range between 1 and 140 nm have been tested by means of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Understanding the diffusion properties in agarose gels is interesting, because such gels are good models for microbial biofilms and cells cytoplasm. The fluorescence correlation spectroscopy technique is very useful for such investigations due to its high sensitivity and selectivity, its excellent spatial resolution compared to the pore size of the gel, and its ability to probe a wide range of sizes of diffusing nanoparticles. The largest hydrodynamic radius (R(c)) of trapped particles that displayed local mobility was estimated to be 70 nm for a 1.5% agarose gel. The results showed that diffusion of particles in agarose gel is anomalous, with a diverging fractal dimension of diffusion when the large particles become entrapped in the pores of the gel. The latter situation occurs when the reduced size (R(A)/R(c)) of the diffusing particle, A, is >0.4. Variations of the fractal exponent of diffusion (d(w)) with the reduced particle size were in agreement with three-dimensional Monte Carlo simulations in porous media. Nonetheless, a systematic offset of d(w) was observed in real systems and was attributed to weak nonelastic interactions between the diffusing particles and polymer fibers, which was not considered in the Monte Carlo simulations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diffusion mechanisms of DNA in agarose gels: NMR studies and Monte Carlo simulations.J Chem Phys. 2022 Jun 28;156(24):245103. doi: 10.1063/5.0092568. J Chem Phys. 2022. PMID: 35778069
-
Diffusion of macromolecules in agarose gels: comparison of linear and globular configurations.Biophys J. 1999 Jul;77(1):542-52. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)76911-0. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10388779 Free PMC article.
-
Anomalous diffusion of poly(ethylene oxide) in agarose gels.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Nov;92:1151-1154. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.054. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 27496604
-
"Flip-flop" orientation of agarose gel fibers in pulsed alternating electric fields.Electrophoresis. 1993 Apr;14(4):355-68. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150140160. Electrophoresis. 1993. PMID: 8500468 Review.
-
Structure and rheology of colloidal particle gels: insight from computer simulation.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2013 Nov;199-200:114-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2013. PMID: 23916723 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of phosphorus bioavailability by iron nanoparticles in a monomictic lake.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 10;8(1):17736. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36103-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30531915 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Dynamics in Composite Hydrogels Exposed to Low-Frequency Focused Ultrasound.Gels. 2023 Sep 22;9(10):771. doi: 10.3390/gels9100771. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37888344 Free PMC article.
-
Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery.Nat Rev Mater. 2016 Dec;1(12):16071. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.71. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Nat Rev Mater. 2016. PMID: 29657852 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of biomolecular diffusion in extracellular matrix condensed by fibroblasts using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 28;8(11):e82382. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082382. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312418 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Recovery of Critical Minerals from Simulated Electronic Wastes Via Reaction-Diffusion Coupling.ChemSusChem. 2025 May 19;18(10):e202402372. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202402372. Epub 2025 Feb 18. ChemSusChem. 2025. PMID: 39907467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abragam, A. 1964. Magnetization of nuclei. Yoshioka Shoten, Kyoto. 67–70.
-
- Amsden, B. 1998. Solute diffusion in hydrogels. An examination of the retardation effect. Polym. Gels Networks. 31:13–43.
-
- Aragon, S. R., and R. Pecora. 1976. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy as a probe of molecular dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 64:1791–1803.
-
- Bouchaud, J. P., and A. Georges. 1990. Anomalous diffusion in disordered media: statistical mechanisms, models and physical applications. Phys. Rep. 195:127–293.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

