Specific versus nonspecific binding of cationic PNAs to duplex DNA
- PMID: 15111421
- PMCID: PMC1304173
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74356-8
Specific versus nonspecific binding of cationic PNAs to duplex DNA
Abstract
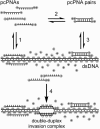
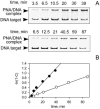
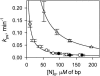
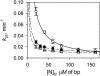
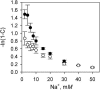
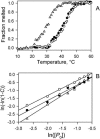
Although peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) are neutral by themselves, they are usually appended with positively charged lysine residues to increase their solubility and binding affinity for nucleic acid targets. Thus obtained cationic PNAs very effectively interact with the designated duplex DNA targets in a sequence-specific manner forming strand-invasion complexes. We report on the study of the nonspecific effects in the kinetics of formation of sequence-specific PNA-DNA complexes. We find that in a typical range of salt concentrations used when working with strand-invading PNAs (10-20 mM NaCl) the PNA binding rates essentially do not depend on the presence of nontarget DNA in the reaction mixture. However, at lower salt concentrations (<10 mM NaCl), the rates of PNA binding to DNA targets are significantly slowed down by the excess of unrelated DNA. This effect of nontarget DNA arises from depleting the concentration of free PNA capable of interacting with DNA target due to adhesion of positively charged PNA molecules on the negatively charged DNA duplex. As expected, the nonspecific electrostatic effects are more pronounced for more charged PNAs. We propose a simple model quantitatively describing all major features of the observed phenomenon. This understanding is important for design of and manipulation with the DNA-binding polycationic ligands in general and PNA-based drugs in particular.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strand invasion by mixed base PNAs and a PNA-peptide chimera.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Sep 1;28(17):3332-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.17.3332. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 10954602 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and mechanism of the DNA double helix invasion by pseudocomplementary peptide nucleic acids.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 30;99(9):5953-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.092127999. Epub 2002 Apr 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11972051 Free PMC article.
-
Extending recognition by peptide nucleic acids (PNAs): binding to duplex DNA and inhibition of transcription by tail-clamp PNA-peptide conjugates.Biochemistry. 2003 Dec 2;42(47):13996-4003. doi: 10.1021/bi035194k. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14636068
-
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) binding-mediated gene regulation.Cell Res. 2004 Apr;14(2):111-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290209. Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15115611 Review.
-
Peptide nucleic acids (PNA) and PNA-DNA chimeras: from high binding affinity towards biological function.Biol Chem. 1998 Aug-Sep;379(8-9):1045-52. Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9792437 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-stranded γPNAs for in vivo site-specific genome editing via Watson-Crick recognition.Curr Gene Ther. 2014;14(5):331-42. doi: 10.2174/1566523214666140825154158. Curr Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 25174576 Free PMC article.
-
Programmable Genome Editing Tools and their Regulation for Efficient Genome Engineering.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2017 Jan 12;15:146-160. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2016.12.006. eCollection 2017. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 28179977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence specificity at targeting double-stranded DNA with a γ-PNA oligomer modified with guanidinium G-clamp nucleobases.Artif DNA PNA XNA. 2010 Jul;1(1):45-53. doi: 10.4161/adna.1.1.12444. Artif DNA PNA XNA. 2010. PMID: 21687526 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature-assisted cyclic hybridization (TACH): an improved method for supercoiled DNA hybridization.Mol Biotechnol. 2010 Jun;45(2):171-9. doi: 10.1007/s12033-010-9261-x. Mol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20238183
-
Labeling DNA for single-molecule experiments: methods of labeling internal specific sequences on double-stranded DNA.Nanoscale. 2011 Aug;3(8):3027-39. doi: 10.1039/c1nr10280j. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Nanoscale. 2011. PMID: 21734993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson, C. F., and M. T. Record, Jr. 1990. Ion distributions around DNA and other cylindrical polyions: theoretical descriptions and physical implications. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Chem. 19:423–465. - PubMed
-
- Bentin, T., and P. E. Nielsen. 1996. Enhanced peptide nucleic acid binding to supercoiled DNA: possible implications for DNA “breathing” dynamics. Biochemistry. 35:8863–8869. - PubMed
-
- Braunlin, W. H., T. J. Strick, and M. T. Record, Jr. 1982. Equilibrium dialysis studies of polyamine binding to DNA. Biopolymers. 21:1302–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

