Association of low p16INK4a and p15INK4b mRNAs expression with their CpG islands methylation with human hepatocellular carcinogenesis
- PMID: 15112341
- PMCID: PMC4622765
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i9.1276
Association of low p16INK4a and p15INK4b mRNAs expression with their CpG islands methylation with human hepatocellular carcinogenesis
Abstract
Aim: To study the significance of p16 and p15 transcription suppression with hypermethylation of their genes' 5'CpG islands during human hepatocellular carcinogenesis.
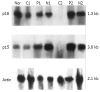
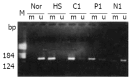
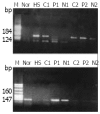
Methods: The mRNA expression levels of p16 and p15 genes were evaluated in cancerous, para-cancerous and non-cancerous tissues of 20 HCC, 3 normal liver tissues from 3 accidentally died healthy adults using semi-quantitatively Northern blot. The methylation status was also assessed with methylation specific PCR.
Results: p16 mRNA expression level was decreased in the cancerous tissues in 60% (12/20) of HCC patients, of which 2 cases had no p16 mRNA detected, 5 cases (25%) displayed variation in the order of cancerous<para-cancerous<non-cancerous liver tissues. p15 mRNA expression level was decreased in the cancerous tissues in 50% (10/20) HCC patients, of which one case had no p15 mRNA detected, 4 cases (20%) displayed variation in the order of cancerous<para-cancerous<non-cancerous liver tissues. In cancerous, para-cancerous and non-cancerous tissues, p16 promoter CpG islands hypermethylation occurred 65%, 60% and 35%, while p15 promoter CpG islands hypermethylation occurred 50%, 40% and 25%. Of 12 HCCs with lower p16 mRNA expression level, 11 cases showed p16 promoter CpG islands methylation (91.6%). Hundred percent (10/10) HCCs with lower p15 mRNA expression level showed p15 promoter CpG islands methylation. Significant correlation between 5'CpG islands methylation and p16/p15 mRNA expression suppression was found. The decreased expression of p16/p15 mRNA or methylation of p16/p15 promoters 5'CpG island was significantly correlate with poor differentiation of HCC (P=0.0083, 0.0102, 0.00271, 0.0218, respectively, P<0.05).
Conclusion: p16 and p15 genes transcriptional inactivation might play an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis. 5'CpG islands methylation might be the major mechanism of p16 and p15 genes inactivation in primary HCC in the studied population. 5'CpG islands methylation of p16 and p15 genes might be an early event in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methylation profiling of twenty promoter-CpG islands of genes which may contribute to hepatocellular carcinogenesis.BMC Cancer. 2002 Nov 15;2:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-2-29. Epub 2002 Nov 15. BMC Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12433278 Free PMC article.
-
Infrequent mutations and no methylation of CDKN2A (P16/MTS1) and CDKN2B (p15/MTS2) in hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan.Eur J Cancer. 1998 Oct;34(11):1789-95. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(98)00189-0. Eur J Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9893670
-
p16 is a major inactivation target in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer. 2000 Jul 1;89(1):60-8. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20000701)89:1<60::aid-cncr9>3.0.co;2-3. Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10897001
-
[Abnormality of p15(INK4b) gene and myelodysplastic syndrome].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2002 Aug;10(4):362-5. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12513775 Review. Chinese.
-
Molecular mechanism underlying the functional loss of cyclindependent kinase inhibitors p16 and p27 in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 21;14(11):1734-40. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1734. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18350604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RLIM suppresses hepatocellular carcinogenesis by up-regulating p15 and p21.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 15;8(47):83075-83087. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20904. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137325 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the methylation patterns of the p16 INK4A, p15 INK4B, and APC genes in gastric adenocarcinoma patients from a Brazilian population.Tumour Biol. 2013 Aug;34(4):2127-33. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0742-y. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23504555
-
Tumor suppressor and hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 21;14(11):1720-33. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1720. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18350603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the Effect of 5-Aza-2'-Deoxycytidine in Comparison to and in Combination with Trichostatin A on p16INK4a, p14ARF, p15INK4b Gene Expression, Cell Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction in Colon Cancer Caco-2 Cell Line.Int J Prev Med. 2021 Jun 25;12:64. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_11_20. eCollection 2021. Int J Prev Med. 2021. PMID: 34447506 Free PMC article.
-
The innovative regularity and role of p16 methylation in blood during HCC development.J Cancer. 2018 Apr 27;9(11):1925-1931. doi: 10.7150/jca.23968. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29896276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ortega S, Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cyclin D-dependent kinases, INK4 inhibitors and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1602:73–87. - PubMed
-
- Serrano M, Hannon GJ, Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 1993;366:704–707. - PubMed
-
- Hannon GJ, Beach D. p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGF-beta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature. 1994;371:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg RA. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995;81:323–330. - PubMed
-
- Hui AM, Sakamoto M, Kanai Y, Ino Y, Gotoh M, Yokota J, Hirohashi S. Inactivation of p16INK4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1996;24:575–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

