Evaluation of effect of hybrid bioartificial liver using end-stage liver disease model
- PMID: 15112365
- PMCID: PMC4622789
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i9.1379
Evaluation of effect of hybrid bioartificial liver using end-stage liver disease model
Abstract
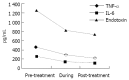
Aim: To study the role of hybrid bioartificial liver (HBL) in clearing proinflammatory cytokines and endotoxin in patients with acute and sub-acute liver failure and the effects of HBL on systemic inflammatory syndrome (SIRS) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS).
Methods: Five cases with severe liver failure (3 acute and 2 subacute) were treated with HBL. The clinical signs and symptoms, total bilirubin (TBIL), serum ammonia, endotoxin TNF-alpha, IL-6 and prothrombin activity (PTA),cholinesterase (CHE) were recorded before, during and after treatment. The end-stage liver disease (MELD) was used for the study.
Results: Two patients were bridged for spontaneous recovery and 1 patient was bridged for OLT successfully. Another 2 patients died on d 8 and d 21. The spontaneous recovery rate was 30.0%. PTA and CHE in all patients were significantly increased (P<0.01), while the serum TBIL, endotoxin, TNF-alpha, IL-6 were decreased. MELD score (mean 43.6) predicted 100% deaths within 3 mo before treatment with HBL. After treatment with HBL, four out of 5 patients had decreased MELD scores (mean 36.6). The MELD score predicted 66% mortalities.
Conclusion: The proinflammatory cytokines (TNFalpha, IL-6 and endotoxin)can be significantly removed by hybrid bioartificial liver and HBL appears to be effective in blocking SIRS and MODS in patients with acute and sub-acute liver failure. MELD is a reliable measure for predicting short-term mortality risk in patients with end-stage liver disease. The prognostic result also corresponds to clinical outcome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Predictive value of pediatrics end-stage liver disease or model for end-stage liver disease score in the prognosis of pediatric acute liver failure treated with artificial liver support system].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Apr;53(4):280-4. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26182503 Chinese.
-
[The organ protective effects and timing of continuous blood purification in the treatment of severe sepsis:a double-blind randomized controlled trial].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 Mar;28(3):241-5. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 29917338 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines and media and peptide hormones during multiple organ dysfunction syndrome following acute abdominal diseases].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2003 Jan;15(1):19-22. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2003. PMID: 12852809 Chinese.
-
Use of the molecular adsorbent recirculating system (MARS™) for the management of acute poisoning with or without liver failure.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011 Nov;49(9):782-93. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2011.624102. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011. PMID: 22077243 Review.
-
Artificial and bioartificial liver support: a review of perfusion treatment for hepatic failure patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Mar 14;13(10):1516-21. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i10.1516. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17461442 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic review: extracorporeal bio-artificial liver-support system for liver failure.Hepatol Int. 2012 Oct;6(4):670-83. doi: 10.1007/s12072-012-9352-9. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Hepatol Int. 2012. PMID: 26201519
References
-
- Fifth conference of national contagious disease and parasitic dis-ease Guideline: prevention and treatment of virus hepatitis (draft) Zhonghua Neike Zazhi. 1995;34:788–791.
-
- Qiu HB, Zhou SX, Yang Y. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrom predictors of mortality and clinical therapetic strategies. Linchuang Jjijiuy Yixue. 2001;10:13–16.
-
- Fry DE, Pearlstein L, Fulton RL, Polk HC. Multiple system organ failure. The role of uncontrolled infection. Arch Surg. 1980;115:136–140. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman JE, Knaus WA, Sun X, Wagner DP. Severity stratification and outcome prediction for multisystem organ failure and dysfunction. World J Surg. 1996;20:401–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials