Efficacy of orlistat as an adjunct to behavioral treatment in overweight African American and Caucasian adolescents with obesity-related co-morbid conditions
- PMID: 15112907
- PMCID: PMC3341614
- DOI: 10.1515/jpem.2004.17.3.307
Efficacy of orlistat as an adjunct to behavioral treatment in overweight African American and Caucasian adolescents with obesity-related co-morbid conditions
Abstract
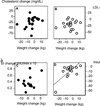
This pilot study compared the efficacy of orlistat as an adjunctive treatment for obesity between African American and Caucasian adolescents. Twenty obese adolescents with obesity-related co-morbid conditions underwent measurements of body composition, glucose homeostasis by frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test (FSIGT), and fasting lipids before and after 6 months treatment with orlistat 120 mg tid in conjunction with a comprehensive behavioral program. Weight (p < 0.05), BMI (p < 0.001), total cholesterol (p < 0.001), LDL cholesterol (p < 0.001), fasting insulin (p < 0.02) and fasting glucose (p < 0.003) were lower after treatment. Insulin sensitivity, measured during the FSIGT, improved significantly (p < 0.02), as did fasting indices such as the homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (p < 0.01). African American subjects exhibited significantly less improvement in weight (p < 0.05), BMI (p < 0.01), waist circumference (p = 0.03), and insulin sensitivity (p = 0.05). Improvements in cholesterol were not significantly different between African Americans and Caucasians. We conclude that Caucasians lost more weight and had greater improvements in insulin sensitivity than African Americans, but both exhibited improvements in plasma lipids. The true benefit of orlistat treatment over a comprehensive behavioral program remains to be determined in placebo-controlled trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three-month tolerability of orlistat in adolescents with obesity-related comorbid conditions.Obes Res. 2002 Jul;10(7):642-50. doi: 10.1038/oby.2002.87. Obes Res. 2002. PMID: 12105286 Clinical Trial.
-
Latin-American trial of orlistat for weight loss and improvement in glycaemic profile in obese diabetic patients.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2003 May;5(3):180-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1463-1326.2003.00262.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2003. PMID: 12681025 Clinical Trial.
-
[Pharmacological therapy of obesity].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008 Apr;9(4 Suppl 1):83S-93S. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008. PMID: 18773755 Italian.
-
Orlistat: its current status as an anti-obesity drug.Eur J Pharmacol. 2002 Apr 12;440(2-3):109-17. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(02)01422-x. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12007529 Review.
-
Modern medical management of obesity: the role of pharmaceutical intervention.J Am Diet Assoc. 1998 Oct;98(10 Suppl 2):S23-6. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8223(98)00706-8. J Am Diet Assoc. 1998. PMID: 9787732 Review.
Cited by
-
Orlistat: a review of its use in the management of patients with obesity.Drugs. 2004;64(24):2845-64. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464240-00010. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15563254 Review.
-
An evolving scientific basis for the prevention and treatment of pediatric obesity.Int J Obes (Lond). 2014 Jul;38(7):887-905. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.49. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014. PMID: 24662696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The stability of metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Dec;94(12):4828-34. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-2665. Epub 2009 Oct 16. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19837941 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of pediatric obesity: consensus position statement of the Italian Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology and the Italian Society of Pediatrics.Ital J Pediatr. 2018 Jul 31;44(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0525-6. Ital J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30064525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Weight-based teasing in youth: Associations with metabolic and inflammatory markers.Pediatr Obes. 2021 Mar;16(3):e12729. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12729. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Pediatr Obes. 2021. PMID: 33059389 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002;288:1728–1732. - PubMed
-
- Must A, Strauss RS. Risks and consequences of childhood and adolescent obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23(Suppl 2):S2–S11. - PubMed
-
- Maffeis C. Aetiology of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. Eur J Pediatr. 2000;159(Suppl 1):S35–S44. - PubMed
-
- Jeffery RW, Drewnowski A, Epstein LH, et al. Long-term maintenance of weight loss: current status. Health Psychol. 2000;19:5–16. - PubMed
-
- Haddock C, Shadish W, Klesges R, Stein R. Treatments for childhood and adolescent obesity. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 1994;16:235–244.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
