Corticosterone influences on Mammalian neonatal sensitive-period learning
- PMID: 15113251
- PMCID: PMC1868531
- DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.118.2.274
Corticosterone influences on Mammalian neonatal sensitive-period learning
Abstract
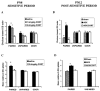
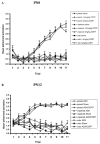
Infant rats exhibit sensitive-period odor learning characterized by olfactory bulb neural changes and odor preference acquisitions critical for survival. This sensitive period is coincident with low endogenous corticosterone (CORT) levels and stress hyporesponsivity. The authors hypothesized that low corticosterone levels modulate sensitive-period learning. They assessed the effects of manipulating CORT levels by increasing and removing CORT during (Postnatal Day 8) and after (Postnatal Day 12) the sensitive period. Results show that (a) exogenous CORT prematurely ends sensitive-period odor-shock-induced preferences; (b) adrenalectomy developmentally extends the sensitive period as indicated by odor-shock-induced odor-preference learning in older pups, whereas CORT replacement can reinstate fear learning; and (c) CORT manipulation modulates olfactory bulb correlates of sensitive-period odor learning in a manner consistent with behavior.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual circuitry for odor-shock conditioning during infancy: corticosterone switches between fear and attraction via amygdala.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 21;26(25):6737-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0499-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16793881 Free PMC article.
-
Early-life stress disrupts attachment learning: the role of amygdala corticosterone, locus ceruleus corticotropin releasing hormone, and olfactory bulb norepinephrine.J Neurosci. 2009 Dec 16;29(50):15745-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4106-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 20016090 Free PMC article.
-
Unique neural circuitry for neonatal olfactory learning.J Neurosci. 2004 Feb 4;24(5):1182-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4578-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14762136 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent model of infant attachment learning and stress.Dev Psychobiol. 2010 Nov;52(7):651-60. doi: 10.1002/dev.20482. Dev Psychobiol. 2010. PMID: 20730787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The development and neurobiology of infant attachment and fear.Dev Neurosci. 2012;34(2-3):101-14. doi: 10.1159/000336732. Epub 2012 May 8. Dev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22571921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developing a sense of safety: the neurobiology of neonatal attachment.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Dec;1008:122-31. doi: 10.1196/annals.130.013. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 14998878 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal presence serves as a switch between learning fear and attraction in infancy.Nat Neurosci. 2006 Aug;9(8):1004-6. doi: 10.1038/nn1733. Epub 2006 Jul 9. Nat Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16829957 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-Induced Chronic Visceral Pain of Gastrointestinal Origin.Front Syst Neurosci. 2017 Nov 22;11:86. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00086. eCollection 2017. Front Syst Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29213232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term colonic hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by neonatal unpredictable vs predictable shock.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007 Sep;19(9):761-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2007.00955.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007. PMID: 17727395 Free PMC article.
-
Dual circuitry for odor-shock conditioning during infancy: corticosterone switches between fear and attraction via amygdala.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 21;26(25):6737-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0499-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16793881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexis MN, Kitraki E, Spanou K, Stylianopoulou F, Sekeris C. Ontogeny of the glucocorticoid receptor in the rat brain. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 1990;265:269–276. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Bauman MD, Capitanio JP, Lavenex P, Mason WA, Mauldin-Jourdain ML, Mendoza SP. The amygdala: Is it an essential component of the neural network for social cognition? Neuropsychologia. 2003;41:517–522. - PubMed
-
- Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Zhou FM, Priest CA, Ennis M, Shipley MT. Tonic and synaptically evoked presynaptic inhibition of sensory input to the rat olfactory bulb via GABAB heteroreceptors. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2000;84:489–494. - PubMed
-
- Barr GA. Ontogeny of nociception and antinociception. NIDA Research Monograph. 1995;158:172–201. - PubMed

