Augmented pulmonary IL-4 and IL-13 receptor subunit expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia
- PMID: 15113854
- PMCID: PMC1770295
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2003.012799
Augmented pulmonary IL-4 and IL-13 receptor subunit expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Some idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs) are characterised by fibroproliferation and deposition of extracellular matrix. Because efficacious treatment options are limited, research has been directed towards understanding the cytokine networks that may affect fibroblast activation and, hence, the progression of certain IIPs.
Aims: To examine the expression of interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-13, and their corresponding receptor subunits in the various forms of IIP and normal patient groups.
Methods: Molecular and immunohistochemical analysis of IL-4, interferon gamma (IFNgamma), IL-13, IL-4 receptor (IL-R), and IL-13 receptor subunits in surgical lung biopsies (SLBs) from 39 patients (21 usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), six non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), eight respiratory bronchiolitic interstitial lung disease (RBILD), and five normal controls).
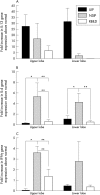
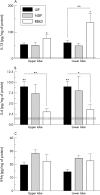
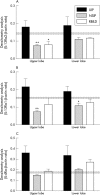
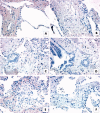
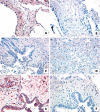
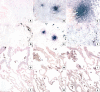
Results: Molecular analysis demonstrated that IL-13Ralpha2, IL-13Ralpha1, and IL-4Ralpha were present in a greater proportion of upper and lower lobe biopsies from patients with UIP than patients with NSIP and RBILD. Immunohistochemical analysis of patients with UIP, NSIP, and RBILD revealed interstitial staining for all three receptor subunits, whereas such staining was only seen in mononuclear cells present in normal SLBs. Fibroblastic foci in patients with UIP strongly stained for IL-4Ralpha and IL-13Ralpha2. Localised expression of IL-4Ralpha was also seen in SLBs from patients with NSIP but not in other groups.
Conclusion: Some histological subtypes of IIP are associated with increased pulmonary expression of receptor subunits responsive to IL-4 and IL-13. These findings may be of particular importance in understanding the pathogenesis of IIP and, more importantly, may provide important novel therapeutic targets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human pulmonary fibroblasts exhibit altered interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 receptor subunit expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.Am J Pathol. 2004 Jun;164(6):1989-2001. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63759-5. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15161635 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of IL-4- and IL-13-responsive cells in pulmonary fibrosis.Immunol Res. 2004;30(3):339-49. doi: 10.1385/IR:30:3:339. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15531774 Review.
-
Focal interstitial CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.J Clin Pathol. 2006 Jan;59(1):28-39. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.026872. J Clin Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16394278 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic attenuation of pulmonary fibrosis via targeting of IL-4- and IL-13-responsive cells.J Immunol. 2003 Sep 1;171(5):2684-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.5.2684. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12928422
-
Possible Roles of Interleukin-4 and -13 and Their Receptors in Gastric and Colon Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 13;22(2):727. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020727. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33450900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The perplexing role of RAGE in pulmonary fibrosis: causality or casualty?Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021 Jan-Dec;15:17534666211016071. doi: 10.1177/17534666211016071. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021. PMID: 34275342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAIL-Dependent Resolution of Pulmonary Fibrosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Jan 24;2018:7934362. doi: 10.1155/2018/7934362. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 29670467 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis, etiology and regulation.Mucosal Immunol. 2009 Mar;2(2):103-21. doi: 10.1038/mi.2008.85. Epub 2009 Jan 7. Mucosal Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19129758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting interleukin-13 with tralokinumab attenuates lung fibrosis and epithelial damage in a humanized SCID idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis model.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 May;50(5):985-94. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0342OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24325475 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic Exercise Attenuated Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis in Th2-Dominant Mice.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 27;11(9):e0163420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163420. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27677175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Douglas W, Ryu J, Schroeder D. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Impact of oxygen and colchicine, prednisone, or no therapy on survival. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161:1172–8. - PubMed
-
- Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Lynch JP, et al. Steroids in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a prospective assessment of adverse reactions, response to therapy, and survival. Am J Med 2001;110:278–82. - PubMed
-
- Ryu JH, Colby TV, Hartman TE. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: current concepts. Mayo Clin Proc 1998;73:1085–101. - PubMed
-
- du Bois RM, Wells AU. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J Suppl 2001;32:43s–55s. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
