Focal nodular hyperplasia with concomitant hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report and clonal analysis
- PMID: 15113871
- PMCID: PMC1770286
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2003.012823
Focal nodular hyperplasia with concomitant hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report and clonal analysis
Erratum in
- J Clin Pathol. 2004 Jul;57(7):784
Abstract
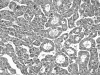
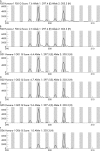
This report describes a hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with concomitant focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) in a 56 year old Chinese man. There were two well circumscribed tumours measuring 3 x 2.5 x 2 cm and 2 x 1.5 x 1.5 cm. The larger mass was grey and soft with a small area of bleeding and necrosis and an intact capsule. The smaller mass was yellow and had no capsule. Clonal analysis was carried out to clarify the relation between the HCC and the adjacent FNH. The clonal analysis was based on the methylation pattern of the polymorphic X chromosome linked androgen receptor gene (HUMARA). In FNH, after HpaII digestion, the allelic bands showed two well defined peaks. The intensity of the two peaks in the DNA from cirrhotic tissue did not differ significantly, consistent with a random pattern of X chromosome inactivation. However, in HCC, after HpaII digestion, the allelic bands differed significantly in intensity. Therefore, there was a typical polyclonal pattern of inactivation in FNH but the HCC was interpreted as being monoclonal.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with focal nodular hyperplasia. Report of a case with clonal analysis.Virchows Arch. 2001 Apr;438(4):408-11. doi: 10.1007/s004280000348. Virchows Arch. 2001. PMID: 11355178
-
Telangiectatic focal nodular hyperplasia: a variant of hepatocellular adenoma.Gastroenterology. 2004 May;126(5):1323-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.02.005. Gastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15131793
-
Use of X-chromosome inactivation pattern and laser microdissection to determine the clonal origin of focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver.Pathology. 2009;41(4):348-55. doi: 10.1080/00313020902885029. Pathology. 2009. PMID: 19404847
-
A case of hepatocellular carcinoma arising within large focal nodular hyperplasia with review of the literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Oct 28;12(40):6567-71. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6567. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17072995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous presence of focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma: case report and review of the literature.Tumori. 2003 Jul-Aug;89(4):434-6. doi: 10.1177/030089160308900417. Tumori. 2003. PMID: 14606650 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in stem cell-derived technologies for hepatocellular carcinoma.Stem Cells Cloning. 2010 May 3;3:81-92. doi: 10.2147/sccaa.s6886. Stem Cells Cloning. 2010. PMID: 24198513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal nodular hyperplasia coexistent with hepatoblastoma in a 36-d-old infant.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 21;21(3):1028-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.1028. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25624742 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell origins and animal models of hepatocellular carcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2010 May;55(5):1241-50. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-0861-x. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19513833 Review.
-
Liver stem cells: implications for hepatocarcinogenesis.Stem Cell Rev. 2005;1(3):253-60. doi: 10.1385/SCR:1:3:253. Stem Cell Rev. 2005. PMID: 17142862 Review.
-
Arrival time parametric imaging using Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography is useful for the detection of spoke-wheel patterns of focal nodular hyperplasia smaller than 3 cm.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Jun;5(6):1551-1554. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1048. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 23837029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen BN, Flejou JF, Terris B, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver: a comprehensive pathologic study of 305 lesions and recognition of a new histologic form. Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1441–54. - PubMed
-
- Saul SH, Titelbaum DS, Gansler TS, et al. The fibrolamellar variant of hepatocellular carcinoma: its association with FNH. Cancer 1987;60:3047–55. - PubMed
-
- Saxena R, Humphreys S, Williams R, et al. Nodular hyperplasia surrounding fibrolamellar carcinoma: a zone of arterialized liver parenchyma. Histopathology 1994;25:275–8. - PubMed
-
- Chen TC, Chou TB, Ng KF, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with focal nodular hyperplasia. Report of a case with clonal analysis. Virchows Arch 2001;438:408–11. - PubMed
-
- Sood AK, Buller RE. Genomic instability in ovarian cancer: a reassessment using an arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction. Oncogene 1996;13:2499–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
