Meiosis-specific yeast Hop1 protein promotes synapsis of double-stranded DNA helices via the formation of guanine quartets
- PMID: 15115800
- PMCID: PMC419448
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh559
Meiosis-specific yeast Hop1 protein promotes synapsis of double-stranded DNA helices via the formation of guanine quartets
Abstract
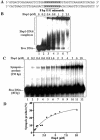
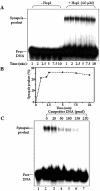
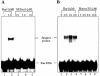
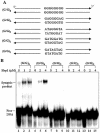
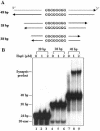
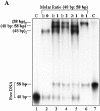
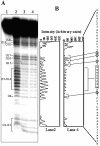
In most eukaryotes, genetic exchange between paired homologs occurs in the context of a tripartite proteinaceous structure called the synaptonemal complex (SC). Genetic analyses have revealed that the genes encoding SC proteins are vital for meiotic chromosome pairing and recombination. However, the number, nature and/or the mechanism used by SC proteins to align chromosomes are yet to be clearly defined. Here, we show that Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hop1, a component of SC, was able to promote pairing of double-stranded DNA helices containing arrays of mismatched G/G sequences. Significantly, pairing was rapid and robust, independent of homology in the arms flanking the central G/G region, and required four contiguous guanine residues. Furthermore, data from truncated DNA double helices showed that 20 bp on either side of the 8 bp mismatched G/G region was essential for efficient synapsis. Methylation interference indicated that pairing between the two DNA double helices involves G quartets. These results suggest that Hop1 is likely to play a direct role in meiotic chromosome pairing and recombination by its ability to promote synapsis between double-stranded DNA helices containing arrays of G residues. To our knowledge, Hop1 is the first protein shown to promote synapsis of DNA double helices from yeast or any other organism.
Figures

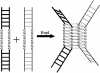
References
-
- Roeder G.S. (1997) Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango. Genes Dev., 11, 2600–2621. - PubMed
-
- Zickler D. and Kleckner,N. (1999) Meiotic chromosomes: integrating structure and function. Annu. Rev. Genet., 33, 603–754. - PubMed
-
- Sym M. and Roeder,G.S. (1994) Crossover interference is abolished in the absence of a synaptonemal complex protein. Cell, 79, 283–292. - PubMed
-
- Bishop D.K., Park,D., Xu,L. and Kleckner,N. (1992) DMC1: a meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation and cell cycle progression. Cell, 69, 439–456. - PubMed
-
- Leu J.-Y. and Roeder,G.S. (1999) The pachytene checkpoint in S. cerevisiae depends on Swe1-mediated phosphorylation of the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc28. Mol. Cell, 4, 805–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

