Membrane protease proteomics: Isotope-coded affinity tag MS identification of undescribed MT1-matrix metalloproteinase substrates
- PMID: 15118097
- PMCID: PMC406442
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0305862101
Membrane protease proteomics: Isotope-coded affinity tag MS identification of undescribed MT1-matrix metalloproteinase substrates
Abstract
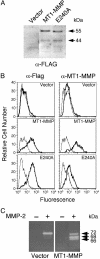
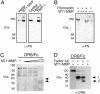
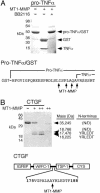
By proteolytic modification of low abundant signaling proteins and membrane receptors, proteases exert potent posttranslational control over cell behavior at the postsecretion level. Hence, substrate discovery is indispensable for understanding the biological role of proteases in vivo. Indeed, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), long associated with extracellular matrix degradation, are increasingly recognized as important processing enzymes of bioactive molecules. MS is now the primary proteomic technique for detecting, identifying, and quantitating proteins in cells or tissues. Here we used isotopecoded affinity tag labeling and multidimensional liquid chromatography inline with tandem MS to identify MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma cell proteins shed from the cell surface or the pericellular matrix and extracellular proteins that were degraded or processed after transfection with human membrane type 1-MMP (MT1-MMP). Potential substrates were identified as those having altered protein levels compared with the E240A inactive MT1-MMP mutant or vector transfectants. New substrates were biochemically confirmed by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight MS and Edman sequencing of cleavage fragments after incubation with recombinant soluble MT1-MMP in vitro. We report many previously uncharacterized substrates of MT1-MMP, including the neutrophil chemokine IL-8, secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor, pro-tumor necrosis factor alpha, death receptor-6, and connective tissue growth factor, indicating that MT1-MMP is an important signaling protease in addition to its traditionally ascribed roles in pericellular matrix remodeling. Moreover, the high-throughput and quantitative nature of isotope-coded affinity tag labeling combined with tandem MS sequencing is a previously undescribed degradomic screen for protease substrate discovery that should be generally adaptable to other classes of protease for exploring proteolytic function in complex and dynamic biological contexts.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protease degradomics: mass spectrometry discovery of protease substrates and the CLIP-CHIP, a dedicated DNA microarray of all human proteases and inhibitors.Biol Chem. 2004 Jun;385(6):493-504. doi: 10.1515/BC.2004.058. Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15255181
-
Identification of candidate angiogenic inhibitors processed by matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) in cell-based proteomic screens: disruption of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/heparin affin regulatory peptide (pleiotrophin) and VEGF/Connective tissue growth factor angiogenic inhibitory complexes by MMP-2 proteolysis.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;27(24):8454-65. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00821-07. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17908800 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacoproteomics of a metalloproteinase hydroxamate inhibitor in breast cancer cells: dynamics of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-mediated membrane protein shedding.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Aug;28(15):4896-914. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01775-07. Epub 2008 May 27. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18505826 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic validation of protease drug targets: pharmacoproteomics of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor drugs using isotope-coded affinity tag labelling and tandem mass spectrometry.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(3):263-70. doi: 10.2174/138161207779313524. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17313360 Review.
-
Degradomics: systems biology of the protease web. Pleiotropic roles of MMPs in cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006 Mar;25(1):69-75. doi: 10.1007/s10555-006-7890-0. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006. PMID: 16680573 Review.
Cited by
-
DR6 as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in adult sarcoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036525. Epub 2012 May 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22567163 Free PMC article.
-
The cysteine-rich domain of the secreted proprotein convertases PC5A and PACE4 functions as a cell surface anchor and interacts with tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Nov;16(11):5215-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-06-0504. Epub 2005 Aug 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16135528 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases in the CNS: interferons get nervous.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Aug;76(16):3083-3095. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03171-9. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31165203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of shear stress and cyclic strain on Sp1 phosphorylation by protein kinase Czeta modulates membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase in endothelial cells.Endothelium. 2008 Jan-Feb;15(1):33-42. doi: 10.1080/10623320802092260. Endothelium. 2008. PMID: 18568943 Free PMC article.
-
Use of protease proteomics to discover granzyme B substrates.Immunol Res. 2005;32(1-3):143-53. doi: 10.1385/IR:32:1-3:143. Immunol Res. 2005. PMID: 16106065 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

