Acetabular reconstruction in developmental hip dysplasia using reinforcement ring with a hook
- PMID: 15118840
- PMCID: PMC3456938
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-004-0559-9
Acetabular reconstruction in developmental hip dysplasia using reinforcement ring with a hook
Abstract
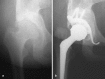
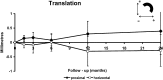
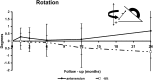
We followed prospectively 27 patients with severe acetabular bone-stock deficiencies due to developmental dysplasia of the hip. Mean preoperative patient age was 56 (34-78) years, mean Harris hip score was 31 (16-66) points and pre-operative mean acetabular angle of Sharp was 47 degrees (34 degrees - 61 degrees). Operative acetabular reconstruction was performed in 28 hips using reinforcement ring with a hook placed in the true acetabulum and autologous bone grafting. A 2-year clinical and radiological follow-up was available in 27 hips. Mean Harris hip score improved to 91 (70-100) points. There were no clinical or radiological signs of aseptic loosening in 25 hips, and the bone graft was radiologically incorporated in all hips. In 24 hips, a radiostereometric analysis showed low rates of non-progressive translation and rotation in 21 reinforcement rings. Three rings showed progressive translation and/or rotation at the 2-year follow-up and were rated probably loose.
Nous avons suivi 27 malades avec des déficiences acétabulaires sévères dû à une dysplasie de développement de la hanche. L’âge moyen préopératoire des malades était de 56 ans (34–78), le score moyen de Harris était de 31 points (16–66) et l’angle moyen de Sharp préopératoire était de 47° (34°–61°). La reconstruction acétabulaire a été exécutée dans 28 hanches en utilisent un anneau de renforcement avec crochet, placé dans le paléo-cotyle, avec greffe osseuse autologue. Un suivi clinique et radiologique de 2 années était disponible pour 27 hanches. Le score moyen de Harris a été amélioré à 91 points (70–100). Il n’y avait pas de signe clinique ou radiologique de descellement aseptique dans 25 hanches et la greffe osseuse était incorporée dans toutes les hanches. Dans 24 hanches une analyse radiostéréométrique a montré un faible taux de translation et de rotation, non progressive, de 21 anneaux de renforcement. Trois anneaux ont montré une translation et/ou une rotation progressive au cours du suivi de 2 années et ont été considérés comme descellés.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Total hip arthroplasty with use of an acetabular reinforcement ring in patients who have congenital dysplasia of the hip. Results at five to fifteen years.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998 Jul;80(7):969-79. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199807000-00005. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. PMID: 9698001
-
Acetabular reconstruction in developmental dysplasia of the hip: results of the acetabular reinforcement ring with hook.J Arthroplasty. 1999 Feb;14(2):131-7. doi: 10.1016/s0883-5403(99)90115-8. J Arthroplasty. 1999. PMID: 10065716
-
Reconstruction of the Shallow Acetabulum With a Combination of Autologous Bulk and Impaction Bone Grafting Fixed by Cement.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Feb;475(2):387-395. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-5107-6. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27837399 Free PMC article.
-
Periacetabular osteotomy in the treatment of severe acetabular dysplasia. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 Mar;88 Suppl 1 Pt 1:65-83. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.00887. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. PMID: 16510801 Review.
-
[Acetabular reconstruction using acetabular reinforcement rings].Orthopade. 1998 Jun;27(6):366-74. doi: 10.1007/pl00003508. Orthopade. 1998. PMID: 9697144 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Current concept in dysplastic hip arthroplasty: Techniques for acetabular and femoral reconstruction.World J Orthop. 2014 Sep 18;5(4):412-24. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i4.412. eCollection 2014 Sep 18. World J Orthop. 2014. PMID: 25232518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Midterm Results of Severe Hip Dysplasia after Using a Cementless Acetabular Component with Bulk Bone Graft in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Minimum Five-Year Follow-Up Study.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Aug 19;11(8):841. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080841. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199799 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence of hip and knee arthroplasty studies to RSA standardization guidelines. A systematic review.Acta Orthop. 2014 Sep;85(5):447-55. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2014.934187. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Acta Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24954489 Free PMC article.
-
Favorable survival of acetabular reconstruction with bone impaction grafting in dysplastic hips.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008 Feb;466(2):359-65. doi: 10.1007/s11999-007-0048-8. Epub 2008 Jan 10. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. PMID: 18196418 Free PMC article.
-
[Total hip replacement in developmental dysplasia: anatomical features and technical pitfalls].Orthopade. 2011 Jun;40(6):543-53. doi: 10.1007/s00132-011-1754-1. Orthopade. 2011. PMID: 21562860 German.
References
-
- Bayan A, Orec R, Pitto RP (2004) Bone grafting and reinforcement ring with hook for acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br [Suppl] (in press)
-
- Charnley J (1979) Low friction arthroplasty of the hip. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
-
- Crowe J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

