The functions of budding yeast Sae2 in the DNA damage response require Mec1- and Tel1-dependent phosphorylation
- PMID: 15121837
- PMCID: PMC400471
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.10.4151-4165.2004
The functions of budding yeast Sae2 in the DNA damage response require Mec1- and Tel1-dependent phosphorylation
Abstract
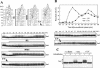
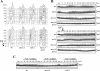
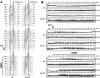
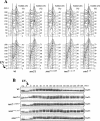
DNA damage checkpoint pathways sense DNA lesions and transduce the signals into appropriate biological responses, including cell cycle arrest, induction of transcriptional programs, and modification or activation of repair factors. Here we show that the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sae2 protein, known to be involved in processing meiotic and mitotic double-strand breaks, is required for proper recovery from checkpoint-mediated cell cycle arrest after DNA damage and is phosphorylated periodically during the unperturbed cell cycle and in response to DNA damage. Both cell cycle- and DNA damage-dependent Sae2 phosphorylation requires the main checkpoint kinase, Mec1, and the upstream components of its pathway, Ddc1, Rad17, Rad24, and Mec3. Another pathway, involving Tel1 and the MRX complex, is also required for full DNA damage-induced Sae2 phosphorylation, that is instead independent of the downstream checkpoint transducers Rad53 and Chk1, as well as of their mediators Rad9 and Mrc1. Mutations altering all the favored ATM/ATR phosphorylation sites of Sae2 not only abolish its in vivo phosphorylation after DNA damage but also cause hypersensitivity to methyl methanesulfonate treatment, synthetic lethality with RAD27 deletion, and decreased rates of mitotic recombination between inverted Alu repeats, suggesting that checkpoint-mediated phosphorylation of Sae2 is important to support its repair and recombination functions.
Figures



References
-
- Abraham, R. T. 2001. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 15:2177-2196. - PubMed
-
- Alcasabas, A. A., A. J. Osborn, J. Bachant, F. Hu, P. J. Werler, K. Bousset, K. Furuya, J. F. Diffley, A. M. Carr, and S. J. Elledge. 2001. Mrc1 transduces signals of DNA replication stress to activate Rad53. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:958-965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
