Network of dynamic interactions between histone H1 and high-mobility-group proteins in chromatin
- PMID: 15121851
- PMCID: PMC400478
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.10.4321-4328.2004
Network of dynamic interactions between histone H1 and high-mobility-group proteins in chromatin
Abstract
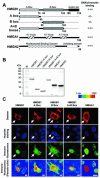
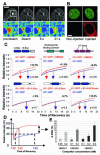
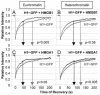
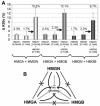
Histone H1 and the high-mobility group (HMG) proteins are chromatin binding proteins that regulate gene expression by modulating the compactness of the chromatin fiber and affecting the ability of regulatory factors to access their nucleosomal targets. Histone H1 stabilizes the higher-order chromatin structure and decreases nucleosomal access, while the HMG proteins decrease the compactness of the chromatin fiber and enhance the accessibility of chromatin targets to regulatory factors. Here we show that in living cells, each of the three families of HMG proteins weakens the binding of H1 to nucleosomes by dynamically competing for chromatin binding sites. The HMG families weaken H1 binding synergistically and do not compete among each other, suggesting that they affect distinct H1 binding sites. We suggest that a network of dynamic and competitive interactions involving HMG proteins and H1, and perhaps other structural proteins, constantly modulates nucleosome accessibility and the local structure of the chromatin fiber.
Figures

References
-
- Agresti, A., and M. E. Bianchi. 2003. HMGB proteins and gene expression. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 13:170-178. - PubMed
-
- Ashar, H. R., M. Schoenberg Fejzo, A. Tkachenko, X. Zhou, J. A. Fletcher, S. Weremowicz, C. C. Morton, and K. Chada. 1995. Disruption of the architectural factor HMGI-C: DNA-binding AT hook motifs fused in lipomas to distinct transcriptional regulatory domain. Cell 82:57-65. - PubMed
-
- Battista, S., F. Pentimalli, G. Baldassarre, M. Fedele, V. Fidanza, C. M. Croce, and A. Fusco. 2003. Loss of Hmga1 gene function affects embryonic stem cell lympho-hematopoietic differentiation. FASEB J. 17:1496-1498. - PubMed
-
- Beaujean, N., C. Bouniol-Baly, C. Monod, K. Kissa, D. Jullien, N. Aulner, C. Amirand, P. Debey, and E. Kas. 2000. Induction of early transcription in one-cell mouse embryos by microinjection of the non-histone chromosomal protein HMG-I. Dev. Biol. 221:337-354. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
