Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (3Dpol): pre-steady-state kinetic analysis of ribonucleotide incorporation in the presence of Mg2+
- PMID: 15122878
- PMCID: PMC2426923
- DOI: 10.1021/bi035212y
Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (3Dpol): pre-steady-state kinetic analysis of ribonucleotide incorporation in the presence of Mg2+
Abstract
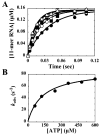
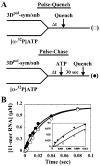
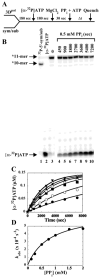
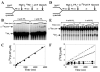
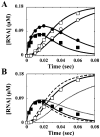
We have solved the complete kinetic mechanism for correct nucleotide incorporation catalyzed by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from poliovirus, 3D(pol). The phosphoryl-transfer step is flanked by two isomerization steps. The first conformational change may be related to reorientation of the triphosphate moiety of the bound nucleotide, and the second conformational change may be translocation of the enzyme into position for the next round of nucleotide incorporation. The observed rate constant for nucleotide incorporation by 3D(pol) (86 s(-1)) is dictated by the rate constants for both the first conformational change (300 s(-1)) and phosphoryl transfer (520 s(-1)). Changes in the stability of the "activated" ternary complex correlate best with changes in the observed rate constant for incorporation resulting from modification of the nucleotide. With the exception of UTP, the K(d) values for nucleotides are at least 10-fold lower than the cellular concentration of the corresponding nucleotide. Our data predict that transition mutations should occur at a frequency of 1/15000, transversion mutations should occur at a frequency of less than 1/150000, and incorporation of a 2'-deoxyribonucleotide with a correct base should occur at a frequency 1/7500. Together, these data support the conclusion that 3D(pol) is actually as faithful as an exonuclease-deficient, replicative DNA polymerase. We discuss the implications of this work on the development of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors for use as antiviral agents.
Figures


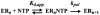
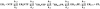
References
-
- Jonckheere H, Anne J, De Clercq E. The HIV-1 reverse transcription (RT) process as target for RT inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2000;20:129–154. - PubMed
-
- Tarrago-Litvak L, Andreola ML, Nevinsky GA, Sarih-Cottin L, Litvak S. The reverse transcriptase of HIV-1: From enzymology to therapeutic intervention. FASEB J. 1994;8:497–503. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq E. HIV inhibitors targeted at the reverse transcriptase. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 1992;8:119–134. - PubMed
-
- Furman PA, Painter GR, Anderson KS. An analysis of the catalytic cycle of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: Opportunities for chemotherapeutic intervention based on enzyme inhibition. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000;6:547–567. - PubMed
-
- Kati WM, Johnson KA, Jerva LF, Anderson KS. Mechanism and fidelity of HIV reverse transcriptase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:25988–25997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

