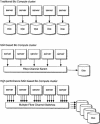
The Ensembl computing architecture
- PMID: 15123594
- PMCID: PMC479128
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1866304
The Ensembl computing architecture
Abstract
Ensembl is a software project to automatically annotate large eukaryotic genomes and release them freely into the public domain. The project currently automatically annotates 10 complete genomes. This makes very large demands on compute resources, due to the vast number of sequence comparisons that need to be executed. To circumvent the financial outlay often associated with classical supercomputing environments, farms of multiple, lower-cost machines have now become the norm and have been deployed successfully with this project. The architecture and design of farms containing hundreds of compute nodes is complex and nontrivial to implement. This study will define and explain some of the essential elements to consider when designing such systems. Server architecture and network infrastructure are discussed with a particular emphasis on solutions that worked and those that did not (often with fairly spectacular consequences). The aim of the study is to give the reader, who may be implementing a large-scale biocompute project, an insight into some of the pitfalls that may be waiting ahead.
Figures



References
-
- Altschul, S., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E., and Lipman, D. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403-410. - PubMed
-
- Fox, G., Williams, R., and Messina, P. 1994. Parallel computing works. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, CA.
-
- Knaff, A. 2003. Udpcast. http://udpcast.linux.lu.
-
- Moore, G. 1965. Cramming more components onto integrated circuits. Electronics 38: 114-117.
-
- Needleman, S.B. and Wunsch, C.D. 1970. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 48: 443-453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
