A skin-selective homing mechanism for human immune surveillance T cells
- PMID: 15123746
- PMCID: PMC2211907
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20032177
A skin-selective homing mechanism for human immune surveillance T cells
Abstract
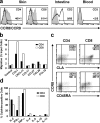
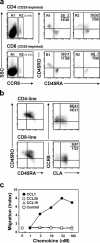
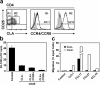
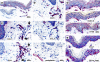
Effective immune surveillance is essential for maintaining protection and homeostasis of peripheral tissues. However, mechanisms controlling memory T cell migration to peripheral tissues such as the skin are poorly understood. Here, we show that the majority of human T cells in healthy skin express the chemokine receptor CCR8 and respond to its selective ligand I-309/CCL1. These CCR8(+) T cells are absent in small intestine and colon tissue, and are extremely rare in peripheral blood, suggesting healthy skin as their physiological target site. Cutaneous CCR8(+) T cells are preactivated and secrete proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma, but lack markers of cytolytic T cells. Secretion of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-10, and transforming growth factor-beta was low to undetectable, arguing against a strict association of CCR8 expression with either T helper cell 2 or regulatory T cell subsets. Potential precursors of skin surveillance T cells in peripheral blood may correspond to the minor subset of CCR8(+)CD25(-) T cells. Importantly, CCL1 is constitutively expressed at strategic cutaneous locations, including dermal microvessels and epidermal antigen-presenting cells. For the first time, these findings define a chemokine system for homeostatic T cell traffic in normal human skin.
Figures


References
-
- Von Andrian, U.H., and C.R. Mackay. 2000. T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N. Engl. J. Med. 343:1020–1034. - PubMed
-
- Moser, B., and P. Loetscher. 2001. Lymphocyte traffic control by chemokines. Nat. Immunol. 2:123–128. - PubMed
-
- Kunkel, E.J., and E.C. Butcher. 2002. Chemokines and the tissue-specific migration of lymphocytes. Immunity. 16:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Dewald, B., M. Thelen, and M. Baggiolini. 1988. Two transduction sequences are necessary for neutrophil activation by receptor agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 263:16179–16184. - PubMed
-
- Sallusto, F., D. Lenig, R. Förster, M. Lipp, and A. Lanzavecchia. 1999. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature. 401:708–712. - PubMed

