The MHC class I-like Fc receptor promotes humorally mediated autoimmune disease
- PMID: 15124024
- PMCID: PMC398424
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI18838
The MHC class I-like Fc receptor promotes humorally mediated autoimmune disease
Abstract
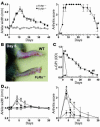
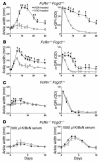
The MHC class I family-like Fc receptor, FcRn, is normally responsible for extending the life span of serum IgG Ab's, but whether this molecule contributes to autoimmune pathogenesis remains speculative. To determine directly whether this function contributes to humoral autoimmune disease, we examined whether a deficiency in the FcRn heavy chain influences autoimmune arthritis in the K/BxN mouse model. FcRn deficiency conferred either partial or complete protection in the arthritogenic serum transfer and the more aggressive genetically determined K/BxN autoimmune arthritis models. The protective effects of an FcRn deficiency could be overridden with excessive amounts of pathogenic IgG Ab's. The therapeutic saturation of FcRn by high-dose intravenous IgG (IVIg) also ameliorated arthritis, directly implicating FcRn blockade as a significant mechanism of IVIg's anti-inflammatory action. The results suggest that FcRn is a potential therapeutic target that links the initiation and effector phases of humoral autoimmune disease.
Figures
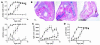
References
-
- Takai T. Roles of Fc receptors in autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002;2:580–592. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 1996;85:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Lee DM, Weinblatt ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001;358:903–911. - PubMed
-
- Simister NE, Mostov KE. An Fc receptor structurally related to MHC class I antigens. Nature. 1989;337:184–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

