Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 is a novel mediator of apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells
- PMID: 15125883
- PMCID: PMC3315378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ghir.2003.12.009
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 is a novel mediator of apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells
Abstract
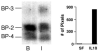
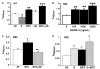
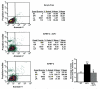
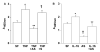
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) is emerging as a critical regulator of cell survival. There has been no study which directly examined the potential role for this major growth factor in the programmed cell death (apoptosis) of insulin-secreting cells. To determine whether IGFBP-3 mediates apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells, we performed a rigorous series of experiments with the rat insulinoma (RIN) cell line m5F and the hamster insulin-secreting tumor (HIT) T-15. Within 24 h exogenous IGFBP-3 induced significant DNA fragmentation in RIN and HIT cells, at doses ranging from 4.4 to 2000 ng/ml (P<0.05) without a classic dose-response relationship. DNA fragmentation induced by rhIGFBP-3 occurred in the presence of immunoglobulin to block the type 1 IGF receptor. As detected by flow cytometry for Annexin V exposure to the cell surface, rhIGFBP-3 treatment doubled the proportion of apoptotic HIT cells from 1.7 +/- 0.4% (serum-free control) to 3.4 +/- 0.2% (P<0.02), an effect completely reversed by co-treatment with 1000 ng/ml rhIGF-I. Immunofluorescent microscopy disclosed that pro-inflammatory Th1 cytokines increased intranuclear aggregation of endogenous IGFBP-3. Cytokine-induced DNA fragmentation was completely blocked by relatively brief pre-treatment with antisense IGFBP-3 phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. In conclusion, we have presented the first evidence that IGFBP-3 contributes to cytokine-mediated apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis through a death receptor-mediated pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 15;64(6):2229-37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-1675. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15026367
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 mediates cytokine-induced mesangial cell apoptosis.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2005 Jun;15(3):207-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2005.02.008. Epub 2005 Mar 23. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2005. PMID: 15935983 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 induces apoptosis and mediates the effects of transforming growth factor-beta1 on programmed cell death through a p53- and IGF-independent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 2;272(18):12181-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.18.12181. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9115291
-
Effects of IGF-I and -II, IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) on growth and apoptosis of human osteosarcoma Saos-2/B-10 cells: lack of IGF-independent IGFBP-3 effects.Eur J Endocrinol. 2001 Aug;145(2):213-21. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1450213. Eur J Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11454519
-
Mecasermin rinfabate: insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, mecaserimin rinfibate, rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3.Drugs R D. 2005;6(2):120-7. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200506020-00008. Drugs R D. 2005. PMID: 15777106 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum complexes of insulin-like growth factor-1 modulate skeletal integrity and carbohydrate metabolism.FASEB J. 2009 Mar;23(3):709-19. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-118976. Epub 2008 Oct 24. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 18952711 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin/IGF-driven cancer cell-stroma crosstalk as a novel therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 23;17(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0806-0. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29475434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of Recreational Soccer and Caloric Restricted Diet Reduces Markers of Protein Catabolism and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.J Nutr Health Aging. 2017;21(2):180-186. doi: 10.1007/s12603-015-0708-4. J Nutr Health Aging. 2017. PMID: 28112773 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel actions of IGFBP-3 on intracellular signaling pathways of insulin-secreting cells.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2006 Feb;16(1):41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2005.09.003. Epub 2005 Nov 4. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2006. PMID: 16275148 Free PMC article.
-
Mining the acute respiratory distress syndrome proteome: identification of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)/IGF-binding protein-3 pathway in acute lung injury.Am J Pathol. 2006 Jul;169(1):86-95. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050612. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16816363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vassiliadis S, Dragiotis V, Protopapadakis E, Athanassakis I, Mitlianga P, Konidaris K, et al. The destructive action of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta in IDDM is a multistage process: evidence and confirmation by apoptotic studies, induction of intermediates and electron microscopy. Mediat. Inflamm. 1999;8:85–91. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunger A, Augstein P, Schmidt S, Fischer U. Identification of interleukin-1 induced apoptosis in rat islets using in situ specific labeling of fragmented DNA. J. Autoimmun. 1996;3:309–313. - PubMed
-
- Delaney CA, Pavlovic D, Hoorens A, Pipeleers DG, Eizirik DL. Cytokines induce deoxyribonucleic strand breaks and apoptosis in human pancreatic islet cells. Endocrinology. 1997;138:2610–2614. - PubMed
-
- Sanvito F, Nichols A, Herrera PL, Huarte J, Wohlwend A, Vassalli JD, et al. TGF-beta 1 overexpression in murine pancreas induces chronic pancreatitis and, together with TNF-alpha, triggers insulin-dependent diabetes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995;217:1279–1286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

