Randomised controlled trial of effects of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on heartburn and gastro-oesophageal reflux: Bristol helicobacter project
- PMID: 15126313
- PMCID: PMC421785
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.38082.626725.EE
Randomised controlled trial of effects of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on heartburn and gastro-oesophageal reflux: Bristol helicobacter project
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effects of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on heartburn and gastro-oesophageal reflux.
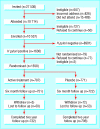
Design: Cross sectional study, followed by a randomised placebo controlled trial.
Setting: Seven general practices in Bristol, England.
Participants: 10,537 people, aged 20-59 years, with and without H pylori infection (determined by the (13)C-urea breath test).
Main outcome measures: Prevalence of heartburn and gastro-oesophageal acid reflux at baseline and two years after treatment to eradicate H pylori infection.
Results: At baseline, H pylori infection was associated with increased prevalence of heartburn (odds ratio 1.14, 95% confidence interval 1.05 to 1.23) but not reflux (1.05, 0.97 to 1.14). In participants with H pylori infection, active treatment had no effect on the overall prevalence of heartburn (0.99, 0.88 to 1.12) or reflux (1.04, 0.91 to 1.19) and did not improve pre-existing symptoms of heartburn or reflux.
Conclusions: H pylori infection is associated with a slightly increased prevalence of heartburn but not reflux. Treatment to eradicate H pylori has no net benefit in patients with heartburn or gastro-oesophageal reflux.
Comment in
-
Eradicating H pylori.BMJ. 2004 Jun 12;328(7453):1388-9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7453.1388. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15191955 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Helicobacter pylori and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: information underlying pathology is not given.BMJ. 2004 Aug 14;329(7462):402. doi: 10.1136/bmj.329.7462.402. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15310618 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Helicobacter pylori and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: important data were not presented.BMJ. 2004 Aug 14;329(7462):402. doi: 10.1136/bmj.329.7462.402-a. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15310619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Helicobacter pylori eradication had no effect on heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux in H pylori infection.ACP J Club. 2004 Nov-Dec;141(3):75. ACP J Club. 2004. PMID: 15518459 No abstract available.
-
Does Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication have any effect on heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux?Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004 Nov;1(1):16-7. doi: 10.1038/ncpgasthep0004. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. PMID: 16265036 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tarpila S, Kekki M, Samloff IM, Sipponen P, Siurala M. Morphology and dynamics of the gastric mucosa in duodenal ulcer patients and their first-degree relatives. Hepatogastroenterology 1983;30: 198-201. - PubMed
-
- Calam J. Clinicians' guide to Helicobacter pylori. London: Chapman & Hall Medical, 1996: 39-77.
-
- Labenz J, Blum AL, Bayerdorffer E, Meining A, Stolte M, Borsch G. Curing Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer may provoke reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology 1997;112: 1442-7. - PubMed
-
- Hamada H, Haruma K, Mihara M, Kamada T, Yoshihara M, Sumii K, et al. High incidence of reflux oesophagitis after eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori: impacts of hiatal hernia and corpus gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000;14: 729-35. - PubMed
-
- Manes G, Mosca S, De Nucci C, Lombardi G, Lioniello M, Balzano A. High prevalence of reflux symptoms in duodenal ulcer patients who develop gastro-oesophageal reflux disease after curing Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Liver Dis 2001;33: 665-70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical