Orthologous gene-expression profiling in multi-species models: search for candidate genes
- PMID: 15128448
- PMCID: PMC416470
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-5-r34
Orthologous gene-expression profiling in multi-species models: search for candidate genes
Abstract
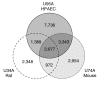
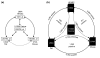
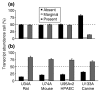
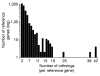
Microarray-driven gene-expression profiles are generally produced and analyzed for a single specific experimental model. We have assessed an analytical approach that simultaneously evaluates multi-species experimental models within a particular biological condition using orthologous genes as linkers for the various Affymetrix microarray platforms on multi-species models of ventilator-associated lung injury. The results suggest that this approach may be a useful tool in the evaluation of biological processes of interest and selection of process-related candidate genes.
Figures

References
-
- Parker JC. Inhibitors of myosin light chain kinase and phosphodiesterase reduce ventilator-induced lung injury. J Appl Physiol. 2000;89:2241–2248. - PubMed
-
- Parker JC, Ivey CL, Tucker A. Phosphotyrosine phosphatase and tyrosine kinase inhibition modulate airway pressure-induced lung injury. J Appl Physiol. 1998;85:1753–1761. - PubMed
-
- Webb HH, Tierney DF. Experimental pulmonary edema due to intermittent positive pressure ventilation with high inflation pressures. Protection by positive end-expiratory pressure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974;110:556–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

