Heat shock protein-mediated resistance to high hydrostatic pressure in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 15128516
- PMCID: PMC404417
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.5.2660-2666.2004
Heat shock protein-mediated resistance to high hydrostatic pressure in Escherichia coli
Abstract
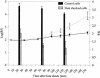
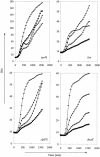
A random library of Escherichia coli MG1655 genomic fragments fused to a promoterless green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene was constructed and screened by differential fluorescence induction for promoters that are induced after exposure to a sublethal high hydrostatic pressure stress. This screening yielded three promoters of genes belonging to the heat shock regulon (dnaK, lon, clpPX), suggesting a role for heat shock proteins in protection against, and/or repair of, damage caused by high pressure. Several further observations provide additional support for this hypothesis: (i). the expression of rpoH, encoding the heat shock-specific sigma factor sigma(32), was also induced by high pressure; (ii). heat shock rendered E. coli significantly more resistant to subsequent high-pressure inactivation, and this heat shock-induced pressure resistance followed the same time course as the induction of heat shock genes; (iii). basal expression levels of GFP from heat shock promoters, and expression of several heat shock proteins as determined by two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins extracted from pulse-labeled cells, was increased in three previously isolated pressure-resistant mutants of E. coli compared to wild-type levels.
Figures


References
-
- Atlung, T., and H. Ingmer. 1997. H-NS: a modulator of environmentally regulated gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 24:7-17. - PubMed
-
- Balny, C., P. Masson, and K. Heremans. 2002. High pressure effects on biological macromolecules: from structural changes to alteration of cellular processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1595:3-10. - PubMed
-
- Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

