Learning at different satiation levels reveals parallel functions for the cAMP-protein kinase A cascade in formation of long-term memory
- PMID: 15128860
- PMCID: PMC6729435
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0669-04.2004
Learning at different satiation levels reveals parallel functions for the cAMP-protein kinase A cascade in formation of long-term memory
Abstract
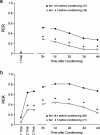
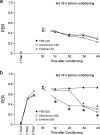
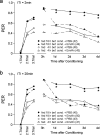
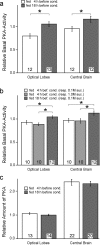
Learning and memory formation in intact animals is generally studied under defined parameters, including the control of feeding. We used associative olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension response in honeybees to address effects of feeding status on processes of learning and memory formation. Comparing groups of animals with different but defined feeding status at the time of conditioning reveals new and characteristic features in memory formation. In animals fed 18 hr earlier, three-trial conditioning induces a stable memory that consists of different phases: a mid-term memory (MTM), translation-dependent early long-term memory (eLTM; 1-2 d), and a transcription-dependent late LTM (lLTM; > or =3 d). Additional feeding of a small amount of sucrose 4 hr before conditioning leads to a loss of all of these memory phases. Interestingly, the basal activity of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), a key player in LTM formation, differs in animals with different satiation levels. Pharmacological rescue of the low basal PKA activity in animals fed 4 hr before conditioning points to a specific function of cAMP-PKA cascade in mediating satiation-dependent memory formation. An increase in PKA activity during conditioning rescues only transcription-dependent lLTM; acquisition, MTM, and eLTM are still impaired. Thus, during conditioning, the cAMP-PKA cascade mediates the induction of the transcription-dependent lLTM, depending on the satiation level. This result provides the first evidence for a central and distinct function of the cAMP-PKA cascade connecting satiation level with learning.
Figures


References
-
- Abel T, Nguyen PV, Barad M, Deuel TAS, Kandel ER, Bourtchouladze R (1997) Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 88: 615–626. - PubMed
-
- Adams JP, Sweatt JD (2002) Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42: 135–163. - PubMed
-
- Beinfeld MC (2001) An introduction to neuronal cholecystokinin. Peptides 22: 1197–2200. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Sahar Y, Robinson GE (2001) Satiation differentially affects performance in a learning assay by nurse and forager honey bees. J Comp Physiol [A] 187: 891–899. - PubMed
-
- Blevins JE, Schwartz MW, Baskin DG (2002) Peptide signals regulating food intake and energy homeostasis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80: 396–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
